Net Promoter Score
Definition
Net Promoter Score (NPS) is a metric used to measure customer loyalty and satisfaction towards a brand, product, or service.
Description
Net Promoter Score (NPS) is a metric used to measure customer loyalty and satisfaction. It is based on the idea that a customer’s likelihood to recommend a company, product or service to others strongly indicates their overall satisfaction.
NPS is calculated by asking customers a single question: “On a scale of 0-10, how likely are you to recommend our company/product/service to a friend or colleague?” Based on their responses, customers are then grouped into three categories: Promoters (score of 9-10), Passives (score of 7-8), and Detractors (score of 0-6).
The NPS is calculated by subtracting the percentage of Detractors from the percentage of Promoters. The resulting score can range from -100 to +100, with a higher score indicating higher customer loyalty and satisfaction.
NPS is a widely used metric in business because it provides a simple and effective way to measure customer satisfaction and loyalty. It allows companies to identify areas where they need to improve and track the effectiveness of their customer experience initiatives over time.
Importance of Net Promoter Score
Net Promoter Score (NPS) is an important business metric, providing valuable insights into customer satisfaction and loyalty. Here are some reasons why NPS is important:
- Predictive of growth: NPS is strongly correlated with business growth. Studies have shown that companies with high NPS scores grow faster and have higher profitability than those with low scores.
- Simple and easy to understand: NPS is a simple and easy-to-understand metric that can be easily communicated across all levels of an organisation. This makes it an effective tool for aligning teams and driving improvements in customer satisfaction.
- Customer-centric: NPS is focused on the customer’s perspective and clearly indicates how likely they are to recommend a company, product or service to others. This helps businesses prioritise their efforts and resources to improve the customer experience.
- Benchmarking: NPS allows companies to benchmark their performance against competitors and industry standards. This provides valuable insights into areas where they need to improve to stay competitive.
- Continuous improvement: NPS is a dynamic metric that can be tracked over time. This allows businesses to monitor the effectiveness of their customer experience initiatives and make ongoing improvements to their products and services.
How to improve Net Promoter Score?
Improving Net Promoter Score (NPS) requires a systematic approach to improving the customer experience. Here are some strategies that businesses can use to improve their NPS:
- Identify the root causes: Analyse feedback from Detractors and identify the root causes of their dissatisfaction. Address these issues systematically and monitor their impact on NPS over time.
- Focus on customer service: Train your employees to provide excellent customer service and handle complaints effectively. Empower them to take ownership of customer issues and resolve them quickly and efficiently.
- Personalise the customer experience: Offer personalised experiences that cater to your customers’ specific needs and preferences. Use data analytics to gain insights into customer behaviour and tailor your offerings accordingly.
- Proactively seek feedback: Solicit customer feedback at multiple touchpoints in the customer journey. Use this feedback to identify areas to improve and make changes accordingly.
- Communicate and act on feedback: Communicate with your customers about your changes based on their feedback. This shows that you are committed to improving the customer experience and can help to increase customer loyalty.
- Reward loyalty: Offer rewards or incentives to customers who refer others to your business. This can increase customer retention and drive new business through referrals.
How is Net Promoter Score calculated?
The Net Promoter Score (NPS) is a customer loyalty metric that measures how likely a customer is to recommend a company’s product or service to others. It is calculated based on the responses to a single survey question: “How likely are you to recommend this product/service to a friend or colleague?”
To calculate the NPS, respondents are first categorised into one of three groups based on their answers to the survey question:
- Promoters: Respondents who answer with a 9 or 10 are considered promoters. They are loyal enthusiasts who keep buying and referring to others, fueling growth.
- Passives: Respondents who answer with a 7 or 8 are considered passive. They are satisfied customers but must be more enthusiastic to promote the product/service actively.
- Detractors: Respondents who answer with a score between 0 and 6 are considered detractors. They are unhappy customers who can damage the brand and impede growth through negative word-of-mouth.
To calculate the NPS, the percentage of detractors is subtracted from the percentage of promoters. The resulting score can range from -100 to 100, with higher scores indicating higher customer loyalty and satisfaction.
Here’s an example of how to calculate NPS:
Suppose a company sends out a survey asking customers how likely they are to recommend their product on a scale of 0-10. The following responses are received:
- 100 customers answered with a 9 or 10 (promoters)
- 50 customers answered with a 7 or 8 (passives)
- 50 customers answered with a 0-6 (detractors)
To calculate the NPS, first, calculate the percentage of detractors and promoters:
- Percentage of detractors = (50/200) x 100 = 25%
- Percentage of promoters = (100/200) x 100 = 50%
Subtract the percentage of detractors from the percentage of promoters to get the NPS:
- NPS = 50% – 25% = 25
In this example, the NPS is 25, which is a good score indicating that the company has more promoters than detractors.
Future Scope of Net Promoter Score.
The Net Promoter Score (NPS) has been widely used by companies to measure customer loyalty and satisfaction, and it will likely continue to be a valuable tool in the future. Here are some potential future developments for NPS:
- Integration with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML): Companies increasingly use AI and ML to analyse customer feedback and identify patterns and insights. Integrating NPS with these technologies could provide a more accurate and efficient way of measuring and analysing customer sentiment.
- Personalization: Companies are increasingly looking to provide personalised experiences to their customers. Using NPS data, companies could tailor their products and services to meet their customers’ specific needs and preferences.
- Expansion beyond customer feedback: While NPS is primarily used to measure customer loyalty and satisfaction, it could also be used to measure employee engagement, supplier satisfaction, and other stakeholder relationships.
- Integration with social media: Social media platforms are increasingly being used by customers to share their opinions about products and services. Integrating NPS with social media analytics could provide companies with a more comprehensive understanding of customer sentiment.
Example
The NPS scores for Amazon that the brand built in its business on providing excellent customer service was 51, considered an exceptional score.
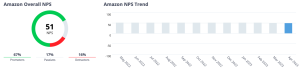
Source: www.comparably.com
FAQ
What is NPS?
NPS is a metric used to measure customer loyalty and satisfaction. It is based on a single survey question that asks customers how likely they are to recommend a company’s product or service to others.
How is NPS calculated?
NPS is calculated by subtracting the percentage of detractors (customers who provide a score of 0-6) from the percentage of promoters (customers who provide a score of 9 or 10). The resulting score can range from -100 to 100, with higher scores indicating higher customer loyalty and satisfaction.
What is a good NPS score?
NPS scores can vary depending on the industry and the specific company. However, a score of 50 or above is generally considered good, while a score of 70 or above is considered excellent.
How can companies use NPS?
Companies can use NPS to measure customer loyalty and satisfaction, identify improvement areas, and track customer sentiment changes over time. They can also use NPS to benchmark themselves against competitors and set improvement goals.
Are there any limitations to NPS?
While NPS is a useful tool for measuring customer loyalty and satisfaction, it has some limitations. For example, it is based on a single survey question and may not comprehensively understand customer sentiment. Additionally, NPS scores can be influenced by factors outside the company’s control, such as market conditions or changes in customer preferences.
How can companies improve their NPS?
To strengthen their NPS, companies can focus on improving customer experience, providing excellent customer service, and addressing customer feedback and complaints promptly and effectively. They can also use NPS data to identify improvement areas and prioritise initiatives that will significantly impact customer loyalty and satisfaction.






We would love to have your opinion.