Return on Investment(ROI)
Return on Investment (ROI)
Definition
ROI stands for Return on Investment, a performance metric used to measure the profitability or effectiveness of an investment.
Description
By calculating ROI, it would be easier to determine an investment’s financial impact or effectiveness. However, this would make it harder for businesses to decide where to allocate their resources and which assets to pursue.
For example, a business might invest significant money in a marketing campaign. Still, without calculating the ROI, it would be difficult to determine whether the movement was worth the investment. As a result, the business might continue investing in marketing without knowing which campaigns drive the most value, leading to wasted resources and missed opportunities.Calculating ROI allows businesses to identify which investments generate the most value and adjust their strategies accordingly. This can help companies to maximise their return on investment and achieve their financial goals more effectively.
ROI is calculated as the ratio of the net profit or gain generated by an asset to the investment cost. It is expressed as a percentage, with higher values indicating more profitability or effectiveness.
The formula to calculate ROI is:
ROI = (Net Profit / Cost of Investment) x 100%
Where:
Net Profit = Revenue generated from the investment minus the cost of the investment Cost of Investment = Total cost of the investment, including any associated expenses such as marketing, production, and distribution costs
The result is expressed as a percentage. A positive ROI indicates that the investment generated a profit, while a negative ROI indicates that the acquisition resulted in a loss.
ROI is widely used in business to evaluate the success of investments in areas such as marketing, capital projects, and new products or services.
Importance of Return On Investment(ROI)
ROI is important for several reasons:
- It helps businesses make informed investment decisions: ROI provides a clear and objective way to measure an investment’s financial success or effectiveness. By calculating ROI, businesses can make informed decisions about which investments to pursue and how to allocate their resources most effectively.
- It enables businesses to optimise their investments: By tracking ROI, businesses can identify which investments are generating the most value and adjust their strategies accordingly. This can help businesses maximise their return on investment and achieve their financial goals more effectively.
- It helps businesses evaluate performance: ROI can be used to evaluate the financial performance of a business or individual investments over time. By tracking ROI, businesses can identify trends, monitor progress, and make adjustments as needed.
- It supports effective budgeting: By knowing the ROI of different investments, businesses can make better decisions about how to allocate their budget. They can focus on investments that generate the most value and avoid investing in projects that are unlikely to be profitable.
How to increase Return On Investment(ROI)?
There are several strategies that businesses can use to increase their ROI:
- Improve efficiency: One way to increase ROI is to improve operational efficiency. This can be done by reducing costs, improving productivity, and streamlining processes.
- Focus on high-value activities: Businesses can increase their ROI by focusing on activities that generate the most value. This might involve reallocating resources to high-value projects or prioritising investments likely to generate the highest return.
- Increase revenue: Another way to increase ROI is to increase revenue. This can be done by expanding into new markets, introducing new products or services, or increasing sales to existing customers.
- Reduce costs: Businesses can also increase their ROI by reducing costs. This might involve renegotiating contracts with suppliers, reducing waste, or finding ways to lower overhead costs.
- Optimise marketing: Businesses can increase their ROI by optimising their marketing efforts. This might involve targeting the right audience, using the right messaging and channels, and tracking performance metrics to identify areas for improvement.
Future Strategies to increase Return On Investment(ROI)
Some future strategies to increase ROI might include:
- Leveraging technology: As technology advances, businesses can use automation, artificial intelligence, and other tools to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and increase revenue. For example, businesses might use AI-powered chatbots to automate customer service or leverage data analytics to optimise pricing and inventory management.
- Investing in employee training and development: By investing in employee training and development, businesses can improve productivity, reduce turnover, and increase the skills and knowledge of their workforce. This can lead to higher quality products and services and enhanced customer satisfaction.
- Embracing sustainability: Consumers increasingly demand sustainable products and services, and businesses that embrace sustainability can often gain a competitive advantage. By reducing waste, using renewable energy sources, and implementing environmentally-friendly practices, businesses can reduce costs, attract customers, and improve their reputation.
- Building strong partnerships: By building strategic partnerships with other businesses, organisations, or communities, businesses can tap into new markets, gain access to new resources, and share expertise and knowledge. This can lead to new opportunities for growth and innovation, as well as increased revenue and profitability.
- Focusing on customer experience: Customer experience is becoming an increasingly important factor in business success. By prioritising customer needs and preferences, businesses can improve customer satisfaction, reduce churn, and increase revenue through repeat business and positive word-of-mouth. This might involve investing in customer service training, leveraging customer data to personalise experiences, and using customer feedback to improve products and services.
Benefits of increasing Return On Investment(ROI)
There are several benefits to increasing ROI:
- Increased profitability: By increasing ROI, businesses can generate more profits and improve their financial position. This can provide more resources for future investments and help the business grow and expand.
- Better resource allocation: Businesses can allocate their resources more effectively by focusing on investments that generate the highest ROI. This can help prevent wasteful spending and ensure that resources are used productively and efficiently.
- Improved competitiveness: Businesses that are able to increase their ROI often gain a competitive advantage over their rivals. This can help the business attract customers, win contracts, and increase market share.
- Enhanced reputation: A strong ROI can enhance the importance of a business, making it more attractive to investors, customers, and employees. This can lead to more opportunities for growth and innovation and improved recruitment and retention of top talent.
- Greater flexibility: A strong ROI can provide businesses with greater flexibility and resilience in the face of economic challenges or market volatility. This can help the business weather difficult times and emerge more robust and more competitive in the long run.
Example
One Indian brand that increased its ROI is Hindustan Unilever Limited (HUL), one of India’s largest consumer goods companies. In 2016, HUL implemented a program called “Winning in Many Indias” to increase sales and profitability by focusing on emerging markets in rural India.
As part of this program, HUL developed a range of products tailored to the needs and preferences of rural consumers, including affordable packaged goods and smaller pack sizes. The company also invested in distribution channels and developed new marketing campaigns for rural consumers.These efforts paid off, with HUL reporting a 12% increase in net profits in the first quarter of 2016, largely driven by increased sales in rural areas. The company’s ROI also improved, with a return of 78% on its investment in rural marketing initiatives.
HUL’s success in increasing ROI through its rural marketing program exemplifies how businesses can achieve strong financial results by targeting underserved markets and tailoring products and services to the needs and preferences of specific customer segments.
FAQ
What is ROI?
ROI stands for Return on Investment. It is a financial metric used to measure the profitability of an investment by calculating the percentage of return relative to the cost of the investment.
Why is ROI important?
ROI is important because it gives businesses a clear picture of how effectively they use their resources to generate profits. By analysing ROI, businesses can identify which investments are most profitable and make more informed decisions about how to allocate their resources in the future.
How is ROI calculated?
ROI is calculated by dividing the net profit of an investment by the cost of the investment and expressing the result as a percentage. The formula for calculating ROI is: ROI = (Net Profit / Cost of Investment) x 100%.
What are some strategies for increasing ROI?
Strategies for increasing ROI include improving efficiency, reducing costs, increasing revenue, optimising pricing and inventory management, investing in employee training and development, embracing sustainability, building strong partnerships, and focusing on customer experience.
Can ROI be negative?
ROI can be negative if the investment cost exceeds the net profit generated. A negative ROI indicates that the investment has not been profitable and may need to be a wise use of resources.
What is a good ROI?
A good ROI depends on the industry and the specific investment. Generally, an ROI of 10% or higher is considered good, while a 20% or higher ROI is considered excellent.
What are some limitations of ROI?
Limitations of ROI include that it needs to account for the time value of money, it may not take into account all relevant costs and benefits, and it may not be a good measure of long-term profitability. Additionally, ROI can be challenging to compare across different investments or industries.
Retargeting
Definition
Retargeting is a digital advertising strategy that targets users who have previously interacted with a brand or visited a website to encourage them to take a desired action.
Description
It is a digital marketing technique that displays targeted ads to people who have previously interacted with a brand or visited a website. It uses tracking technology to collect user behaviour data, such as visited pages, items viewed or added to the cart, and searches made.
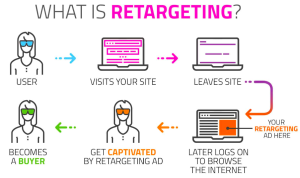 This data is then used to serve personalised ads to these users across various channels, such as social media, search engines, and other websites. It aims to keep the brand or product in mind for these users and ultimately encourage them to purchase or take a desired action.
This data is then used to serve personalised ads to these users across various channels, such as social media, search engines, and other websites. It aims to keep the brand or product in mind for these users and ultimately encourage them to purchase or take a desired action.
Importance of Retargeting
It is an important digital marketing strategy for several reasons:
- Increased conversions: By targeting users who have already shown an interest in a brand or product, retargeting campaigns have a higher chance of converting those users into customers. This is because retargeting ads remind users of their previous interests, encouraging them to return to the website and purchase.
- Improved ROI: Since retargeting campaigns target users more likely to convert, they tend to have a higher ROI than other types of digital advertising. This is because the cost of serving an ad to a retargeted user is typically lower than the cost of acquiring a new user.
- Personalization: It allows brands to serve personalised ads to users based on their previous behaviour. This creates a more relevant and engaging advertising experience, increasing the chances of conversion.
- Brand awareness: Even if a user clicks quickly, retargeting ads can help increase brand awareness and keep that user’s brand in mind. This can lead to future conversions or recommendations to others.
Steps in Retargeting
The following are the general steps involved in a campaign:
- Set up tracking: The first step is to set up tracking technology on your website, such as a tracking pixel or JavaScript code. This will enable you to collect user behaviour data, such as visited pages, items viewed or added to the cart, and searches made.
- Define your audience: Based on the data collected from tracking, you can define your audience. This could include users who have abandoned their cart, visited a specific page, or spent some time on your website.
- Create ad content: Once you have defined your audience, you can create ad content that is relevant to them. This could include product recommendations, promotions, or reminders of items left in their cart.
- Choose your ad platform: There are various ad platforms you can use for retargeting, such as social media, search engines, or display networks. Choose the platform(s) that best match your audience and ad content.
- Set up your campaign: Set up your campaign with the chosen ad platform(s), and select your retargeting audience. You can also set parameters for ad frequency and duration.
- Monitor and optimise your campaign performance regularly, and optimise it as needed. This could include adjusting ad content, targeting parameters, or bidding strategies to improve ad effectiveness and ROI.
Effective Strategies for Retargeting
Here are some effective strategies for retargeting:
- Segment your audience: Divide your audience into segments based on their behaviour on your website. For example, you can create segments for users who have abandoned their cart, viewed a particular product, or spent a certain amount of time on your website. By segmenting your audience, you can create more personalised and relevant ads.
- Use dynamic retargeting: It involves serving ads tailored to the specific products or pages a user has viewed on your website. This creates a more personalised and relevant advertising experience, which can increase the chances of conversion.
- Experiment with ad formats: Test different formats, such as static images, carousel ads, or video ads, to see which ones work best for your audience. Use engaging visuals and compelling copy to grab users’ attention.
- Set frequency caps: Be mindful of how often you serve retargeting ads to users. Setting frequency caps can help avoid ad fatigue and prevent users from feeling annoyed or overwhelmed with your ads.
- Offer incentives: Consider offering discounts, free shipping, or other incentives to entice users to purchase. This can be a powerful motivator for users who are on the fence about buying.
- Test and optimise: Continuously test and optimise your campaigns to improve their effectiveness. This could include adjusting ad content, targeting parameters, or bidding strategies to improve ROI and conversions.
Future Aspects of Retargeting
The future of retargeting is likely to involve the following aspects:
- Advanced audience targeting: As digital advertising technology advances, retargeting campaigns will likely become even more sophisticated in their targeting capabilities. This could include using AI and machine learning to analyse user behaviour and serve personalised ads to users based on their individual preferences and interests.
- Integration with other channels: Retargeting campaigns will likely become more integrated with other marketing channels, such as email and social media. This will enable brands to create a more cohesive and consistent advertising experience across different channels and touchpoints.
- Increased emphasis on privacy: As privacy concerns grow, retargeting campaigns must become more transparent and compliant with data privacy regulations. This could include using first-party data and consent-based marketing to ensure user privacy is respected.
- Focus on customer experience: Retargeting campaigns must create a positive and engaging customer experience rather than simply bombarding users with ads. This could include personalised recommendations, interactive ad formats, and other tactics that make a more engaging and relevant advertising experience.
- Use of new ad formats: Retargeting campaigns will continue experimenting with new ad formats, such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) ads. These immersive ad formats can create a more engaging and memorable user advertising experience, leading to higher engagement and conversions.
Example
Suppose you are browsing through a clothing retailer’s website and add a few items to your cart but ultimately decide to wait to complete the purchase. Later, as you browse the internet or use social media, you notice ads from that retailer featuring the items you added to your cart.
This is an example of retargeting, where the retailer uses cookies or other tracking technologies to identify you as a potential customer who has already shown interest in their products. The retailer hopes to encourage you to return to their website and complete your purchase by serving you with targeted ads.
Many brands use retargeting as part of their digital advertising strategy to stay top-of-mind with potential customers and increase the likelihood of conversion.
FAQ
What is retargeting?
Retargeting is a digital advertising strategy that involves targeting ads to users who have previously interacted with a brand or visited its website.
How does retargeting work?
It uses cookies or other tracking technologies to identify users who have previously interacted with a brand or visited its website. Once these users are identified, the brand can serve them with targeted ads as they browse the internet or use social media.
Why is retargeting important?
It is important because it enables brands to reach users who have already shown interest in their products or services, making them more likely to convert into paying customers.
What are some effective retargeting strategies?
Effective retargeting strategies include segmenting your audience, using dynamic retargeting, experimenting with ad formats, setting frequency caps, offering incentives, and continuously testing and optimising your campaigns.
What are some future trends in retargeting?
Future trends include advanced audience targeting, integration with other marketing channels, increased emphasis on privacy, focus on customer experience, and the use of new ad formats such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) ads.
Is retargeting ethical?
Retargeting can be ethical if it is transparent and respects user privacy. Brands should be clear about their use of tracking technologies and allow users to opt out of retargeting ads if they wish.
Reputation Management
Reputation Management
Definition
Reputation management refers to monitoring and improving the public perception of a brand, organisation, or individual.
Description
It refers to the practice of monitoring and influencing the public perception of an individual or organisation. It involves proactively building a positive image and mitigating any negative feedback or criticism.

Reputation management can include a variety of strategies, such as monitoring online reviews and social media mentions, responding to customer complaints and feedback, promoting positive news and press coverage, and actively engaging with stakeholders to build trust and credibility.
It aims to create a powerful and positive image that accurately reflects the values and mission of the individual or organisation. This can attract new customers, retain existing ones, and build long-term relationships with key stakeholders. It can also help protect against potential crises or negative publicity by establishing a foundation of trust and credibility that can withstand any challenges.
Importance of Reputation Management
Reputation management is crucial for individuals and organizations because it can significantly impact their success and longevity. Here are some reasons why it is important:
- Builds trust and credibility: A positive reputation can establish trust and credibility with customers, partners, investors, and other stakeholders. This can increase loyalty, better relationships, and more growth opportunities.
- Protects against negative publicity: Reputation management can help to mitigate the impact of negative feedback or criticism by responding quickly and effectively. This can prevent a negative narrative from spiralling out of control and damaging the individual or organization’s reputation.
- Attracts new customers and talent: A strong reputation can attract new customers and top talent, who are likelier to do business with or work for a company with a positive image.
- Enhances brand value: Reputation management can increase the value of a brand, as a strong reputation can make it more attractive to potential buyers or investors.
- Improves crisis management: A well-managed reputation can provide a foundation for effective crisis management. In a crisis, a positive reputation can help mitigate the impact and provide a buffer against negative publicity.
Steps for Reputation Management
Here are some steps for effective reputation management:
- Monitor your online reputation: Regularly monitor your online presence, including social media channels, review sites, and search engine results. This can help you identify any negative feedback or criticism and respond promptly.
- Respond to feedback: Respond to both positive and negative feedback promptly and professionally. Acknowledge any concerns or complaints and work to resolve them to the best of your ability.
- Create positive content: Create and promote positive content that accurately reflects your values and mission. This includes blog posts, social media updates, and press releases highlighting your accomplishments and contributions.
- Engage with stakeholders: Engage with your customers, partners, and other stakeholders to build relationships and establish trust. This can include responding to comments, participating in online communities, and attending industry events.
- Monitor your competitors: Keep an eye on your competitors’ online reputation and strategies. This can help you identify potential opportunities or threats and adjust your approach accordingly.
- Address any issues: If a crisis or negative publicity arises, address it quickly and transparently. Be honest about the situation and take steps to rectify any issues. Communicate clearly and frequently to keep stakeholders informed.
- Continuously evaluate and adjust: Regularly evaluate your reputation management strategy and adapt it as needed. Stay up to date with industry trends and best practices and adjust your approach accordingly.
Future aspect of Reputation Management
The future of it is likely to be shaped by several trends and developments, including:
- Increased use of AI and automation: As technology evolves, we expect to see more use in reputation management. This can include tools that help monitor and analyse online feedback, chatbots, and other automated systems for responding to customer inquiries.
- Greater emphasis on transparency and accountability: In an era of increasing scrutiny and accountability, individuals and organisations must be more transparent and proactive in managing their reputations. This can involve greater openness in communication and more robust policies and procedures for addressing issues and concerns.
- Social media platforms will continue to be a key channel for reputation management, with companies and individuals investing more resources in creating and promoting positive content. This will require a deeper understanding of social media dynamics and meaningful engagement with customers and stakeholders.
- Heightened focus on ethical and social responsibility: Consumers and other stakeholders increasingly demand that companies and individuals demonstrate a commitment to ethical and social responsibility. Reputation management strategies will need to align with these values and communicate a clear sense of purpose and impact.
- The emergence of new risks and challenges: Finally, the future of it will be shaped by emerging risks and challenges, including cybersecurity threats, fake news, and the proliferation of deep fakes and other forms of disinformation. Reputation management strategies must be agile and adaptable, able to respond quickly to changing circumstances and protect against new risks.
Example
One example of effective reputation management is how Johnson & Johnson handled the Tylenol tampering crisis in 1982. When it was discovered that someone had tampered with Tylenol bottles in Chicago, resulting in several deaths, Johnson & Johnson took swift and decisive action to protect its customers and reputation.
The company immediately recalled all Tylenol products nationwide and launched a massive public relations campaign to discuss the problem and reassure consumers. Johnson & Johnson also worked closely with law enforcement and the media to investigate the tampering and identify the perpetrator.
Through these actions, Johnson & Johnson was able to maintain the trust and loyalty of its customers and ultimately regain its market share in the over-the-counter pain relief category. The company also implemented new safety measures, such as tamper-evident packaging and increased security, to prevent similar incidents from happening in the future.
This example shows how effective reputation management requires proactive planning, quick and decisive action, and a commitment to transparency and accountability. By responding effectively to a crisis and taking steps to prevent similar incidents from occurring in the future, Johnson & Johnson was able to protect its reputation and maintain the trust of its customers.
FAQ
What is reputation management?
Reputation management involves monitoring and managing an individual or organisation’s online and offline reputation, including its image, credibility, and trustworthiness.
Why is reputation management critical?
A positive reputation can help to attract customers, investors, and partners, while a negative reputation can harm an individual or organisation’s brand and financial performance. Therefore, reputation management is important to protect and enhance an individual or organisation’s reputation and maintain stakeholder trust.
What are the key elements of effective reputation management?
Effective reputation management requires proactive planning, monitoring, and communication. Key elements include monitoring online feedback, responding to feedback promptly and professionally, creating and promoting positive content, engaging with stakeholders, addressing any issues transparently, and continuously evaluating and adjusting the strategy as needed.
How can I improve my online reputation?
To improve your online reputation, you can start monitoring your online presence, including social media channels, review sites, and search engine results. Respond promptly and professionally to feedback or criticism, create and promote positive content, and engage with your customers and other stakeholders to build relationships and establish trust.
What are the risks of not managing your reputation?
Not managing your reputation can lead to a negative image, loss of customers, and damage to your brand and financial performance. Negative feedback or criticism can quickly spread online and offline, and, if not addressed promptly, can harm your reputation and credibility.
Can reputation management be outsourced?
Yes, reputation management can be outsourced to professional agencies or consultants who specialise in this field. However, it is important to choose a reputable and experienced provider who can effectively manage your reputation and communicate with your stakeholders professionally and ethically.
Random Sampling
Definition
Random sampling is a statistical method of selecting a subset of individuals or items from a larger population in which each member has an equal chance of being chosen.
Description
It is a statistical technique to select a representative subset of individuals or items from a larger population. This method involves selecting individuals or items randomly, which means each member of the population has an equal chance of being selected for the sample.
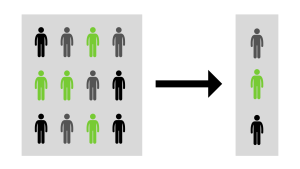
By selecting a sample randomly, the sample is more likely to be representative of the population, and the results obtained from the sample can be generalised to the larger population with greater confidence. It is widely used in research and data analysis to make inferences about a population based on a sample.
Importance of Random Sampling
- Helps to ensure that the sample selected is representative of the larger population.
- Reduces the chances of bias in the sample selection process.
- Increases the chances of obtaining accurate and reliable results.
- Allows for generalisations to be made about the population based on the sample.
- Helps to reduce the cost and time required for data collection by selecting a smaller subset of individuals or items.
- It is widely used in research and data analysis across various fields and industries.
- Provides a basis for statistical inference and hypothesis testing.
- It can help to identify patterns and relationships within the data.
- Helps to improve the validity and reliability of research studies.
- Is essential for ensuring that research findings can be applied to real-world situations.
How to prepare for Random Sampling?
These are the steps to prepare for random sampling:
- Define the population: Clearly define the people you want to study. This will help you determine the sample size you need to select.
- Determine the sample size: Based on the size of the population, determine the sample size you need to select. This can be done using statistical formulas or software.
- Choose a method: There are several methods, including simple random sampling, stratified random sampling, and cluster sampling. Choose the method that is most appropriate for your research study.
- Select the sample: Once you have chosen a method, select the sample using a random number generator or other software. Ensure that each member of the population has an equal chance of being selected.
- Validate the sample: Validate the sample to ensure that it is representative of the larger population. Check for any biases or anomalies that may have affected the sample selection process.
- Analyse the data: Analyse the data obtained from the sample and draw conclusions about the larger population. Use statistical tools to make inferences and generalise the findings to the population.
Future Scope of Random Sampling
It will continue to be an essential statistical method in the future for a variety of reasons:
- It helps to ensure that the sample selected is representative of the larger population, which is essential for making accurate and reliable inferences about the people.
- As data becomes more complex and the number of variables increases, it can reduce the cost and time required for data collection by selecting a smaller subset of individuals or items.
- It can reduce bias in the sample selection process, which is important for ensuring that external factors do not influence the results.
- With the rise of big data and machine learning, it can be used to improve the performance of algorithms by selecting a representative subset of data for training and testing.
- It can also be used in quality control and assurance to ensure that products or services meet the standards set by the larger population.
Example
A brand example of random sampling could be a company that produces a new type of energy drink and wants to know how it is received by consumers. The company could use it to select a representative sample of individuals from the larger population of potential consumers to try the energy drink and provide feedback.
The company could use a simple random sampling method to randomly select individuals from a list of potential consumers or use stratified random sampling to select individuals from different demographics such as age, gender, and location.
FAQ
What is random sampling?
It is a statistical technique to select a representative subset of individuals or items from a larger population. This method involves selecting individuals or entities randomly, which means each member of the population has an equal chance of being selected for the sample.
Why is random sampling necessary?
Random selection is important because it helps to ensure that the sample selected is representative of the larger population, which is essential for making accurate and reliable inferences about the people. By selecting individuals or items randomly, each member of the population has an equal chance of being selected for the sample, which helps to avoid bias and increases the chances of obtaining accurate and reliable results.
What are the different types of random sampling methods?
There are several types of random sampling methods, including simple random sampling, stratified random sampling, and cluster sampling.
How do you select a sample using random sampling?
You can use a random number generator or other software to select a sample using it. Ensure that each member of the population has an equal chance of being selected.
What is the sample size in random sampling?
It is the number of individuals or items selected for the sample. The size of the sample depends on the size of the population and the level of precision required for the study.
Can random sampling be used in qualitative research?
Yes, a random sample can be used in qualitative research, although it is more commonly used in quantitative analysis. In qualitative research, it can be used to select a representative sample of individuals for interviews or focus groups.
How can you validate the sample in random sampling?
To validate the sample, you can check for any biases or anomalies that may have affected the sample selection process. You can also compare the characteristics of the sample to the larger population to ensure that it represents the people.
What are the limitations of random sampling?
The limitations include the potential for sampling error, which can occur when the sample is not representative of the larger population. Additionally, random selection may not be appropriate for specific populations or research questions.
Quality Score
Definition
Quality Score is a metric used in digital advertising, particularly in Google Ads, that measures the quality and relevance of an advertiser’s keywords, ads, and landing pages.
Description
A score between 1 and 10 helps determine the ad’s position in search results and the cost per click (CPC) the advertiser pays. A higher score can lead to a better ad position and lower CPC, while a lower score can result in a lower ad position and higher CPC. The Quality Score is determined by factors such as the ad’s click-through rate (CTR), the ad’s relevance to the keyword, and the landing page quality.

Source: www.google.com
It is based on several factors, including the ad’s click-through rate (CTR), the ad’s relevance to the keyword, and the quality of the landing page. A high-Quality Score indicates that the ad is relevant and valuable to the user. Thus, the search engine rewards the advertiser with a higher ad position and lower CPC. Conversely, a low-Quality Score indicates that the ad is not as relevant to the user’s search, and thus, the advertiser is penalised with a lower ad position and higher CPC.
Improving the score requires optimising the ad, keyword, and landing page for relevance and user experience. This includes writing compelling ad copy, targeting relevant keywords, and ensuring the landing page provides a positive user experience. By improving the score, advertisers can increase the effectiveness of their paid search campaigns and maximise their return on investment.
Importance of Knowing Quality Score in Digital Marketing
Knowing the Quality Score in digital marketing is important for several reasons:
- Ad position and CPC: It affects the ad’s position in search results and the cost per click (CPC) that the advertiser pays. A higher Quality Score leads to a better ad position and lower CPC, while a lower Quality Score can result in a lower ad position and higher CPC.
- Optimization: It provides insights into how well the ad, keyword, and landing page perform. By knowing the score, advertisers can identify areas for improvement and optimise their campaigns for better performance.
- Relevance: It measures the significance of the ad to the user’s search query, ensuring that users are presented with advertisements that are most relevant to their needs. This helps to improve user experience and increase the likelihood of clicks and conversions.
- Competition: It determines ad rank, which affects the competition for ad placement. Advertisers with a higher Quality Score can outrank competitors with a lower Quality Score, leading to better visibility and higher click-through rates.
- Cost-effectiveness: By improving the score, advertisers can increase the effectiveness of their campaigns and maximise their return on investment. This can lead to cost savings and better campaign performance over time.
Strategy to improve quality score in digital marketing?
Improving the Quality Score requires a multi-faceted approach that involves optimising the ad, keyword and landing page for relevance and user experience. Here are some strategies to improve Quality Score:
- Relevant keywords: Use relevant keywords closely related to the ad and the landing page. Make sure to group similar keywords into ad groups and create specific ads for each group.
- Compelling ad copy: Write persuasive ad copy that matches the user’s search query and highlights the unique value proposition of the product or service. Use ad extensions to provide additional information and improve visibility.
- Landing page experience: Ensure that the landing page is relevant to the ad and provides a positive user experience. Optimise the page for speed, clarity, and ease of use, and ensure it provides the information the user is looking for.
- Mobile optimization: With more and more users accessing the web through mobile devices, optimising the landing page for mobile devices is essential. Ensure that the page is mobile-friendly and loads quickly on mobile devices.
- Quality content: Provide high-quality content on the landing page that matches the user’s search query and provides relevant information. Use multimedia such as images and videos to enhance the user experience.
- Improve click-through rate (CTR): A higher CTR indicates that the ad is relevant to the user’s search query. Use compelling ad copy, relevant keywords, and extensions to improve CTR.
- Use negative keywords: Use negative keywords to exclude irrelevant searches and improve ad relevance. Negative keywords ensure the ad is not shown to unlikely convert users.
How will Quality Score impact digital marketing?
In the future, dealing with Quality Score may vary as search engines and digital platforms continue to evolve and incorporate new ranking factors and algorithms. Here are some potential changes that could impact how marketers deal with it:
- AI and machine learning: As artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms become more sophisticated, search engines may be able to analyse user behaviour and ad performance more accurately. This could result in a greater emphasis on user engagement metrics and personalised ad targeting. Hence, the quality score will depend on how satisfied users are.
- Voice search: With the rise of voice assistants like Siri and Alexa, search queries are becoming more conversational and natural. This could lead to a greater emphasis on long-tail keywords and natural language processing in ad targeting.
- Privacy and data protection: With growing concerns over privacy and data protection, search engines may place greater importance on user consent and transparency in data collection and ad targeting.
- Integration with other channels: As digital marketing channels become more integrated, Quality Score may be used to rank ads across multiple platforms and channels. This could lead to greater consistency in ad performance and more efficient targeting across channels.
Example
Though it is difficult to know the quality score of an advertiser but one brand that has shown effective marketing include Flipkart.

Source: www.google.com
Flipkart, an Indian e-commerce company, has consistently been ranked among the top digital advertisers in India. The company has implemented a range of optimization strategies to improve the relevance and performance of its ads, including:
- Relevant keywords: Flipkart uses highly relevant keywords that match the user’s search intent and have high commercial intent. The company profoundly understands its target audience and uses this knowledge to create targeted ad campaigns.
- Compelling ad copy: Flipkart’s ad copy is clear and emphasises the unique value proposition of its products. The company uses ad extensions and site links to provide additional information and improve ad performance.
- Landing page experience: Flipkart’s landing pages are optimised for relevance and user experience. The company uses clear, concise messaging, high-quality images, and a simple user interface to improve conversion rates.
FAQ
What is a Quality Score?
It is a metric used by search engines to measure the relevance and Quality of an ad, keyword, or landing page. It affects the ad rank and cost-per-click (CPC) in paid search advertising.
How is the Quality Score calculated?
It is calculated based on several factors, including the relevance of the ad to the search query, the expected click-through rate (CTR) of the ad, the landing page experience, and the ad’s historical performance.
Why is Quality Score important?
It plays a crucial role in determining the ad rank and CPC of an ad. Ads with higher Quality Scores generally receive better ad positions and lower CPCs than ads with lower Quality Scores. This makes it a crucial factor in optimising the cost and effectiveness of paid search campaigns.
How can I improve my Quality Score?
You can improve your score by focusing on the relevance of your ad to the search query, improving the expected CTR of your ad, optimising the landing page experience, and ensuring that your ads have a strong historical performance.
Can Quality Score affect organic search results?
No, it only affects paid search advertising. Therefore, it does not directly impact organic search results.
What are some tools or resources available to help improve the Quality Score?
Google Ads provides a Quality Score reporting tool that shows the score of your keywords, ads, and landing pages. Additionally, several online resources, such as blogs and forums, offer tips and best practices for improving Quality Scores.
Qualified Lead
Qualified Leads
Definition
Qualified leads are potential customers who have shown a high level of interest in a product or service and have the potential to become paying customers.
Description
These are potential customers who have already shown interest in a product or service and have been identified as having a higher likelihood of becoming paying customers.

These leads have typically engaged with a company in some way, such as filling out a contact form or subscribing to a newsletter, and have provided enough information to be evaluated and segmented by the company’s sales and marketing teams. These are considered more valuable than unqualified leads, as they represent a higher likelihood of conversion and are more likely to be receptive to targeted messaging and sales outreach.
Importance of Qualified Leads
Qualified leads are essential for several reasons:
- Higher conversion rates: These are more likely to become paying customers, as they have shown genuine interest in a product or service and are further along in the buying process. This translates to higher conversion rates and increased revenue for businesses.
- Cost-effective: These are more cost-effective to target and convert than unqualified leads, as they represent a higher likelihood of conversion and require less time and resources.
- Improved targeting: By identifying and targeting qualified leads, businesses can focus their efforts on the most promising prospects and tailor their messaging and outreach to their specific needs and interests.
- Better customer insights: These leads provide valuable insights into customer behaviour and preferences, which can inform product development, marketing strategies, and customer retention efforts.
How to generate Qualified Leads?
There are several ways to generate them:
- Content marketing: Creating high-quality, educational content that addresses your target audience’s pain points and interests can attract qualified leads and position your business as a thought leader in your industry.
- Search engine optimization (SEO): Optimising your website and content for search engines can help potential customers find your business when searching for relevant keywords and phrases.
- Social media marketing: Leveraging social media platforms to engage with your target audience and promote your content can help generate interest and drive leads to your website.
- Email marketing: Sending targeted email campaigns to subscribers who have opted in to receive communications from your business can help nurture leads and move them closer to conversion.
- Referral marketing: Encouraging satisfied customers to refer their friends and colleagues to your business can effectively generate them.
- Paid advertising: Running targeted paid advertising campaigns on search engines and social media platforms can help reach a larger audience and drive more such leads to your website.
- Events and webinars: Hosting events and webinars that provide value to your target audience can help generate these leads and position your business as a thought leader in your industry.
Future of Generating Qualified Leads
The future of these are likely to be shaped by advancements in technology and changes in consumer behaviour. Here are some potential future trends:
- Increased personalisation: As consumers become more accustomed to personalised experiences, businesses must tailor their messaging and outreach to individual needs and preferences to generate them.
- Use of AI and machine learning: Advancements in AI and machine learning will allow businesses to analyse customer data more effectively and generate more accurate predictions about customer behaviour, which can help generate more qualified leads.
- Greater emphasis on customer experience: Businesses prioritising the customer experience are more likely to generate qualified leads, as satisfied customers are more likely to refer friends and colleagues and become repeat customers.
- Integration with chatbots and voice assistants: Chatbots and voice assistants can engage with potential customers and generate qualified leads by providing instant responses to queries and guiding prospects through the buying process.
- Increased focus on ethical data collection and privacy: As concerns around data privacy continue to grow, businesses must ensure that they are collecting and using customer data ethically and transparently to generate qualified leads.
Example
Tata Motors is a leading automotive manufacturer in India. Tata Motors generates qualified leads through a variety of channels like online lead generation forms. Tata Motors’ website includes a dedicated section for customers to fill out online forms to request information on their vehicles, book test drives, and schedule service appointments.
 The brand engages with customers on social media platforms such as Facebook and Twitter, where they post updates about new models, promotions, and customer testimonials.
The brand engages with customers on social media platforms such as Facebook and Twitter, where they post updates about new models, promotions, and customer testimonials.
Tata Motors hosts events and webinars to showcase its latest models and provide education on automotive topics, which can help generate qualified leads. The company encourages satisfied customers to refer their friends and family to their dealership through referral programs, which can help generate qualified leads.
FAQ
What are qualified leads?
These are potential customers who have shown a genuine interest in a company’s products or services and have been vetted by the company’s marketing or sales team as having a higher likelihood of converting into paying customers.
How do I generate qualified leads?
To generate these leads, businesses can use a variety of tactics such as content marketing, email marketing, social media marketing, SEO, PPC advertising, and events. It’s important to tailor these tactics to the specific needs and preferences of the target audience to increase the likelihood of generating qualified leads.
Why are qualified leads important?
These leads are important because they represent potential customers who have already shown interest in a company’s products or services. This means they are more likely to convert into paying customers, which can increase revenue and profitability for the business.
What is the difference between a lead and a qualified lead?
A lead is a potential customer who has expressed interest in a company’s products or services. In contrast, a qualified lead is a lead that has been vetted by the company’s marketing or sales team and deemed more likely to convert into a paying customer.
How can I measure the effectiveness of my qualified lead-generation efforts?
Businesses can use various metrics to measure the effectiveness of their qualified lead generation efforts, including conversion rates, lead quality scores, and customer lifetime value. Tracking these metrics over time and adjusting marketing and sales strategies as needed to optimise results is essential.
How can I nurture my qualified leads?
To nurture qualified leads, businesses can use personalised email marketing, retargeting ads, and personalised content to keep potential customers engaged and move them further along the sales funnel. It’s important to tailor these tactics to the specific needs and preferences of the target audience to increase the likelihood of conversion.
What is the future of qualified leads?
The future of qualified leads is likely to be shaped by advancements in technology and changes in consumer behaviour. This may include greater personalisation, use of AI and machine learning, greater emphasis on customer experience, integration with chatbots and voice assistants, and increased focus on ethical data collection and privacy.
Psychographics
Psychographics
Definition
Psychographics refers to the study of a target audience’s personality, values, attitudes, interests, and lifestyle for marketing purposes.
Description
Psychographics involves analysing people’s psychological and behavioural characteristics to develop more effective marketing strategies.
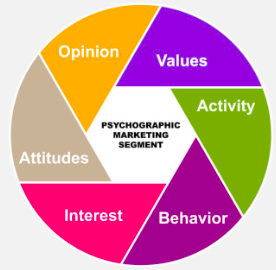
Psychographics can complement demographics, which focuses on observable characteristics such as age, gender, income, and education level. While demographics provide a basic understanding of a target audience, psychographics allows marketers to gain a deeper insight into what motivates and drives consumer behaviour.
Importance of Psychographics
Understanding psychographics is important for marketers because:
- it allows them to gain a deeper insight into their target audience’s motivations, values, and behaviours. By understanding these psychological and behavioural characteristics, marketers can develop more targeted and personalised marketing messages that resonate with their audience on a deeper level.
- In contrast to demographics, which provide basic information about a target audience, psychographics can help marketers understand why their target audience is interested in their products or services and what factors influence their decision-making. This can enable marketers to tailor their marketing messages to their audience’s specific needs and preferences, leading to higher engagement and conversion.
- Psychographic data can segment a target audience into smaller, more specific groups based on shared values, interests, or lifestyle factors. This can help marketers develop targeted campaigns more likely to resonate with each segment, leading to more effective use of marketing resources.
- Understanding psychographics is essential for developing effective marketing strategies that resonate with a target audience on a deeper, more meaningful level. Marketers can increase engagement, loyalty, and conversion rates by using psychographic insights to develop targeted and personalised marketing messages.
Psychographics that marketers Use.
Some standard psychographic variables that marketers may use to understand their target audience include:
- Personality: This refers to an individual’s unique traits and characteristics. Marketers may use personality tests or surveys to identify personality types most likely interested in their products or services.
- Values are the principles and beliefs that guide an individual’s behaviour and decision-making. Marketers may use surveys or focus groups to understand the values most important to their target audience and how their products or services align with those values.
- Attitudes refer to an individual’s overall evaluation or opinion of a particular topic or concept. Marketers may use surveys or social media listening tools to understand the perspectives of their target audience towards their brand or industry.
- Interests: Interests refer to hobbies, activities, and topics a person is passionate about. Marketers may use data on social media engagement or website browsing behaviour to understand the interests of their target audience and tailor their marketing messages accordingly.
- Lifestyle: Lifestyle refers to an individual’s habits, routines, and behaviours related to work, leisure, and personal life. Marketers may use data on spending habits, travel behaviour, or media consumption to understand the lifestyle of their target audience and develop marketing strategies that resonate with their lifestyle choices.
Types of Psychographics
There are several types of psychographics that marketers can use to better understand their target audience. Some of the most common types of psychographics include:
- Personality traits: These refer to the stable and enduring patterns of behaviour, thoughts, and emotions that make up an individual’s personality. Personality traits can be categorised into the “Big Five” factors: openness, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, and neuroticism.
- Values are the principles and beliefs that guide an individual’s behaviour and decision-making. Examples of values include freedom, security, achievement, and tradition.
- Attitudes refer to an individual’s overall evaluation or opinion of a particular topic or concept. For example, an attitude towards environmental issues, social justice, or political ideology.
- Interests: Interests refer to hobbies, activities, and topics a person is passionate about. Examples of interests include sports, music, food, travel, and fashion.
- Lifestyles: Lifestyles refer to an individual’s habits, routines, and behaviours related to work, leisure, and personal life. This includes spending habits, media consumption, and travel behaviour.
Future Aspects of Psychographics
The future of psychographics in marketing looks promising as technological advancements and data analysis continue to provide more sophisticated tools for understanding and targeting audiences based on their psychological and behavioural characteristics.
One future aspect of psychographics is the increasing use of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to analyse large amounts of data and identify patterns and insights related to consumer behaviour. This can give marketers even more nuanced and personalised insights into their target audience, allowing them to develop more effective marketing campaigns and improve customer engagement.
Another future aspect of psychographics is the growing importance of ethical considerations in data collection and analysis. As consumers become more aware of how their personal data is used by companies, there is a greater need for transparent and ethical data collection and analysis practices. This may include obtaining explicit consent from consumers and using data in ways that are consistent with their values and preferences.
Psychographics may also focus more on cross-cultural and global audiences. As businesses increasingly operate in a globalised marketplace, understanding the psychological and behavioural characteristics of diverse audiences from different cultures will become even more critical for effective marketing strategies.
The future of psychographics in marketing looks promising, with opportunities for more sophisticated data analysis, ethical considerations, and cross-cultural insights to help businesses better understand and connect with their audiences.
Example
Nike’s “Just Do It” campaign is based on the psychographic characteristics of its target audience, including individuals passionate about sports, fitness, and self-improvement.
Nike’s messaging and branding focus on empowering and inspiring individuals to push their limits and achieve their goals, regardless of their background or current circumstances. This message resonates with individuals who identify with Nike’s determination, perseverance, and self-improvement values.

In addition, Nike has used psychographics to segment its target audience and develop more targeted marketing campaigns. For example, Nike has developed specific campaigns targeting women, such as the “Better for It” campaign, which focuses on empowering women to achieve their fitness goals and overcome obstacles.
FAQ
What are Psychographics?
Psychographics is the study of the psychological and behavioural characteristics of individuals, including their personality traits, values, attitudes, interests, and lifestyles.
How are psychographics used in marketing?
Psychographics are used in marketing to better understand a target audience and develop more effective and personalised marketing strategies. By understanding their target audience’s psychological and behavioural characteristics, marketers can create messaging and branding that resonates with their audience on a deeper level.
What are some examples of psychographic characteristics?
Examples of psychographic characteristics include personality traits (such as openness, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, and neuroticism), values (such as freedom, security, achievement, and tradition), attitudes (such as environmentalism, social justice, or political ideology), interests (such as sports, music, food, travel, and fashion), and lifestyles (such as spending habits, media consumption, and travel behaviour).
How can businesses collect data on psychographics?
Businesses can collect psychographic data through various methods, such as surveys, focus groups, social media monitoring, and data analysis of customer behaviour and preferences.
Is there a downside to using psychographics in marketing?
One potential downside to using psychographics in marketing is the risk of stereotyping or making assumptions about individuals based on their psychological and behavioural characteristics. Additionally, some consumers may feel uncomfortable with collecting and using personal data for marketing purposes.
How can businesses use psychographics to improve customer engagement?
By using psychographics to understand their target audience, businesses can develop more targeted and personalised marketing strategies that resonate with their audience on a deeper level. This can improve customer engagement and loyalty, as the brand understands and values customers.
Proximity Marketing
Definition
Proximity marketing is a location-based marketing strategy that delivers targeted advertising messages to consumers based on their physical proximity to a business or product.
Description
It relies on wireless technologies such as Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, GPS, and NFC (Near Field Communication) to send messages to mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets.
Source:www.google.com
It can take many forms, including push notifications, in-app messaging, SMS (text message) marketing, and beacon-based advertising. Push notifications are messages on a mobile device when a user is near a particular location or product. In-app messaging involves displaying targeted messages when a user is near a specific area. SMS marketing involves sending text messages to users near a particular location. Beacon-based advertising involves using small Bluetooth devices called beacons to send targeted messages to mobile devices when they are in range.
It can be used in retail stores, shopping malls, airports, museums, and stadiums to deliver targeted advertising messages, promotions, coupons, and other incentives to drive foot traffic, increase sales, and improve the overall customer experience.
This type of marketing increases customer engagement, improved customer targeting, and better ROI (return on investment) for marketing campaigns. It also allows businesses to collect valuable data on customer behaviour and preferences, which can be used to refine marketing strategies and improve business operations.
Importance of Proximity Marketing
It is becoming increasingly important in today’s digital world, as it provides businesses with an effective way to reach customers in a highly targeted and personalised manner. Here are some of the critical benefits and importance of proximity marketing: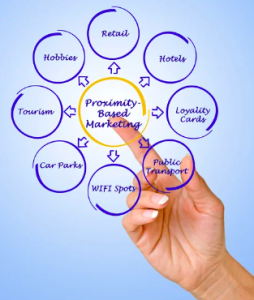
- Increased Customer Engagement: By delivering relevant and personalised messages to customers based on location, it can help businesses engage customers and capture their attention. This can increase brand awareness, customer loyalty, and, ultimately, higher sales.
- Improved Customer Targeting: It allows businesses to target customers with highly relevant messages based on location, interests, and behaviour. This can help enhance marketing campaigns’ effectiveness and increase ROI (return on investment).
- Cost-Effective: It is often more cost effective than traditional forms of advertising, such as TV or print ads. It allows businesses to reach customers in real time, at the exact moment when they are most likely to make a purchase.
- Valuable Data Collection: It provides businesses with valuable data on customer behaviour and preferences, such as how often they visit a store, what products they are interested in, and how long they stay in a particular location. This data can be used to refine marketing strategies and improve business operations.
- Improved Customer Experience: It can help to improve the overall customer experience by providing customers with relevant and personalised messages and offers. This can help to build customer loyalty and drive repeat business.
How to begin with Proximity Marketing?
To begin with proximity marketing, businesses can follow these steps:
- Define your target audience: Identify the target audience you want to reach with your campaign. This can include demographics, location, interests, and behaviours.
- Choose the right technology: Select the right technology for your campaigns, such as beacons, NFC (Near Field Communication), or GPS (Global Positioning System). Each technology has benefits and limitations, so choose the most suitable for your business and target audience.
- Develop a strategy: Develop a strategy for your marketing campaign, including the type of messages you want to deliver, the frequency of messages, and the channels you want to use (e.g., mobile app, text message, email).
- Create engaging content: Create engaging content relevant and personalised to your target audience. This can include offers, promotions, and discounts tailored to their interests and location.
- Implement and test: Implement your marketing campaign to ensure it is working as intended. Monitor the performance of your campaign and make adjustments as needed.
- Analyse and refine: Analyse the data collected from your proximity marketing campaign and refine your strategy based on the results. This can improve the effectiveness of your campaign and drive better results over time.
Types of Proximity Marketing
Businesses can use several types of proximity marketing to engage with customers in a targeted and personalised way. These include:
- Beacon-based marketing: This involves using Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) beacons to deliver targeted messages to customers close to the beacon. These messages can include promotional offers, discounts, and other personalised content.
- NFC-based marketing involves using Near Field Communication (NFC) technology to enable customers to interact with physical objects, such as posters or packaging, using their mobile devices. This can deliver product information, promotions, and other relevant content.
- GPS-based marketing involves using Global Positioning System (GPS) technology to deliver targeted messages to customers based on their location. This can promote nearby businesses, events, or other relevant content.
- Wi-Fi-based marketing: This involves using Wi-Fi networks to deliver targeted messages to customers within a specific Wi-Fi access point. This can promote products, services, or other relevant content.
- QR code-based marketing involves using Quick Response (QR) codes to enable customers to scan a code and receive targeted messages or promotions. This can be used to drive traffic to a specific location or to promote a product or service.
Future Scope of Proximity Marketing
The future of proximity marketing is promising as technological advancements expand their potential. Here are some potential future developments:
- Increased personalisation: As it becomes more advanced, it will enable businesses to deliver even more personalised and relevant messages to customers based on their behaviours, preferences, and real-time context.
- Integration with other technologies: It will likely be integrated with other technologies, such as artificial intelligence, augmented reality, and virtual reality, to create more immersive and engaging customer experiences.
- Expansion of use cases: It will be used in new and creative ways, such as in-store navigation, product recommendations, and gamification.
- Increased use in public spaces: As cities become more intelligent and connected, it will be used more frequently in public spaces, such as museums, parks, and transportation hubs.
- Integration with the Internet of Things (IoT): Proximity marketing will be integrated with IoT devices, such as intelligent home assistants and connected cars, to deliver targeted messages and promotions to customers in new and innovative ways.
Example
Starbucks, the coffee chain, uses a mobile app to connect with customers and offer personalised promotions and rewards based on their location and purchase history. The app uses geofencing technology to detect when a customer is near a Starbucks location and sends notifications about special offers or new menu items. Starbucks uses beacon technology in some stores to send targeted messages and promotions to customers as they browse the store.
FAQ
What is proximity marketing?
It is a form of marketing that uses location-based technologies, such as Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, and GPS, to communicate with customers when they are near a business or specific location.
What are the benefits of proximity marketing?
Engagement, build brand awareness, drive foot traffic to physical locations, and deliver personalised and relevant customer messages are the benefits for this marketing.
What are the types of proximity marketing?
The kinds of proximity marketing include Bluetooth beacons, geofencing, and NFC (near-field communication) technology.
How does proximity marketing work?
Proximity marketing uses a mobile device’s location-based services to detect when a customer is close to a business or location. Once the customer is detected, targeted messages, promotions, or other forms of communication can be sent to their device.
Is proximity marketing intrusive?
Proximity marketing can be seen as intrusive if customers feel their privacy is invaded. However, if done correctly, proximity marketing can be a valuable tool for delivering personalised and relevant messages to customers when they are most likely to engage with a business.
What are some examples of brands using proximity marketing?
Examples of proximity marketing brands include Starbucks, Macy’s, and Walgreens, all of which use mobile apps and location-based technologies to connect with customers and deliver personalised messages and promotions.
What are some best practices for proximity marketing?
Best practices for proximity marketing include getting permission from customers before sending them messages, personalising messages based on customer behaviour and preferences, and delivering relevant and timely messages to maximise engagement.
Programmatic Advertising
Definition
Programmatic advertising is a data-driven approach to buying and selling digital advertising space in real-time using automated software platforms.
Description
It buys and sells digital advertising space using automated technology and real-time bidding. It uses algorithms and data to target specific audiences and serve ads on different channels such as websites, social media, and mobile apps.
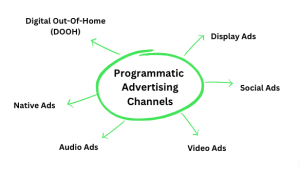
The process involves using a demand-side platform (DSP) to manage ad campaigns and bidding on ad inventory in real time through supply-side platforms (SSPs) or ad exchanges. It is designed to be more efficient and effective than traditional advertising, allowing for precise targeting and optimisation based on data and performance metrics.
Importance of Programmatic Advertising
- Efficiency: It streamlines the ad buying process by automating the entire process, including ad placement, bidding, and optimization. This saves time and resources compared to traditional advertising methods.
- Targeting: It enables advertisers to reach specific audiences using data to target users based on their demographics, behaviour, and interests. This increases the chances of getting the right audience with the right message.
- Real-time optimization: It allows for real-time optimization of ad campaigns, meaning adjustments can be made based on performance data to improve the campaign’s effectiveness.
- Cost-effectiveness: It can be more cost-effective than traditional advertising, as advertisers can set specific budgets and only pay for impressions that reach their target audience.
- Access to data: Provides advertisers with access to data and insights that can be used to refine targeting, optimise ad campaigns, and improve overall performance.
Steps for Programmatic Advertising
- Define campaign objectives: The first step in programmatic advertising is to define the purposes, such as increasing brand awareness, driving traffic to a website, or generating leads.
- Identify target audience: The advertiser needs to identify the target audience based on the campaign objectives. This can be done using data such as demographics, behaviour, and interests.
- Choose ad format and creative: Next, the advertiser needs to choose the ad format and creative used in the campaign. This can include display ads, video ads, native ads, or other structures.
- Set campaign budget: The advertiser needs to set a budget for the campaign, which can be done either as a total spend or as a cost-per-impression (CPM).
- Choose a programmatic platform: The advertiser needs to choose a programmatic platform, such as a demand-side platform (DSP), that will be used to manage the ad campaign and bid on ad inventory.
- Set bidding strategy: The advertiser needs to set a bidding strategy, which determines how much they are willing to pay for each impression or click.
- Launch campaign: The campaign can be launched once all the previous steps have been completed. The programmatic platform will use algorithms and data to bid on ad inventory and serve ads to the target audience in real time.
- Monitor and optimise: After the campaign has launched, the advertiser needs to monitor its performance and make adjustments to optimise the campaign for better results.
Future aspect of Programmatic Advertising
The future of programmatic advertising is expected to see continued growth and innovation. Here are some of the critical aspects that are likely to shape the future:
- Increased automation: It will likely become even more automated, with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) used to optimise real-time ad campaigns.
- Advanced targeting: As data becomes more abundant, it is expected to see even more advanced targeting capabilities, including targeting individuals based on their offline behaviour and purchase history.
- Cross-device targeting: With the proliferation of devices and channels, it will likely focus on cross-device targeting, allowing advertisers to reach the same user across multiple devices.
- Privacy regulations: With increased concerns over data privacy, it is expected to evolve to comply with stricter regulations and user privacy preferences while still providing effective targeting.
- Integration with other technologies: It will likely become more integrated with other technologies, such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), providing new opportunities for immersive and engaging ad experiences.
- Increased use of programmatic TV: It is expected to make further inroads into the TV advertising market, providing more targeted and measurable ad campaigns.
Types of Programmatic Advertising
Advertisers can use several types of programmatic advertising to reach their target audience. Here are some of the most common types:
- Real-time bidding (RTB): This is the most common type of programmatic advertising, where ad inventory is bought and sold in real time through an auction process. Advertisers bid on impressions, and the highest bidder gets their ad served to the user.
- Programmatic direct: This is a type of advertising where advertisers buy ad inventory directly from publishers rather than through an auction process. This allows for more control over ad placement and targeting.
- Private marketplace (PMP): PMPs are invitation-only marketplaces where a select group of advertisers can buy ad inventory directly from publishers. This allows for more premium ad placements and better targeting.
- Automated guaranteed: In this type advertisers buy ad inventory directly from publishers, but the buying process is automated. This allows for more efficient ad buying while maintaining control over ad placement.
- Contextual targeting: It targets users based on the context of their viewing content. For example, an ad for a new car might be served to a user reading an article about cars.
- Behavioural targeting: This type of advertising targets users based on their past online behaviour, such as browsing history and search queries. This allows for more precise targeting based on user interests and preferences.
- Retargeting: Retargeting is targeting users who have previously interacted with a brand, such as visiting a website or adding a product to their cart. This allows for more personalised ad campaigns and can lead to higher conversion rates.
Example
Flipkart has used programmatic advertising to run targeted campaigns across various channels, including display, social media, and video ads. In addition, the company has leveraged data to identify the most effective ad formats and placements for each user, creating a personalised experience that drives engagement and conversion.
Flipkart has also used programmatic advertising to run retargeting campaigns, reaching users who have previously interacted with the brand and showing them relevant products or offers. The company has used dynamic creative optimization (DCO) to automatically adjust ad content based on user behaviour and preferences, delivering more relevant and personalised messages.
FAQ
What is programmatic advertising?
It is buying and selling digital advertising inventory through an automated system that uses data and technology to identify and reach target audiences more efficiently and effectively.
What are the benefits of programmatic advertising?
It allows advertisers to reach their target audience more precisely, with greater control over ad placement and targeting. It also offers improved efficiency and cost-effectiveness, as campaigns can be optimised in real-time based on performance data.
How does programmatic advertising work?
It works through a complex system of ad exchanges, demand-side platforms (DSPs), supply-side platforms (SSPs), and data management platforms (DMPs) that automate the buying and selling of digital ad inventory.
What types of programmatic advertising are there?
Several types of programmatic advertising include real-time bidding (RTB), programmatic direct, private marketplace (PMP), automated guaranteed, contextual targeting, behavioural targeting, and retargeting.
Is programmatic advertising only for display ads?
No, it can be used for various ad formats, including display, video, social media, and even audio ads.
How does programmatic advertising address privacy concerns?
It relies on data to target ads, but privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA require advertisers to obtain user consent and provide transparency around data collection and usage.
How can I measure the success of programmatic advertising campaigns?
Success metrics for programmatic advertising campaigns may include impressions, click-through rates, conversions, and return on ad spend (ROAS). Data and analytics tools can help advertisers measure and optimise real-time campaign performance.
Is programmatic advertising suitable for small businesses?
Yes, programmatic advertising can benefit businesses of all sizes, offering greater targeting precision and efficiency than traditional advertising methods. Small businesses can benefit from programmatic advertising using self-serve platforms or working with a programmatic advertising agency.