Media Buying
Definition
Media buying is purchasing the advertising space or time on various media platforms to reach a target audience.
Description
Media buying is identifying, negotiating, and purchasing advertising space or time on various media platforms such as television, radio, print, outdoor, and digital channels. Media buying aims to reach the target audience in the most cost-effective and efficient manner possible while maximising the return on investment (ROI) for the advertiser.

Source: www.google.com
Media buying involves extensive research, planning, and analysis to determine the most influential media channels and ad placements for the target audience, negotiating favourable rates and monitoring the campaign’s performance to ensure that it meets the advertiser’s goals and objectives.
Importance of Media Buying
Media buying is an essential aspect of any successful advertising campaign, as it helps advertisers reach their target audience most cost-effectively and efficiently. Here are some key reasons why media buying is essential:
- Targeting: Media buying allows advertisers to reach their target audience through carefully selected media channels and ad placements, which increases the likelihood of getting the right people at the right time.
- Cost-effectiveness: Media buying enables advertisers to negotiate favourable rates and maximise their return on investment (ROI) by selecting the most cost-effective media channels and ad placements.
- Reach: Media buying helps advertisers to reach a large and diverse audience across multiple media platforms, including television, radio, print, outdoor, and digital channels.
- Measurement: Media buying provides advertisers with the ability to measure the performance of their advertising campaigns through a range of metrics, including reach, frequency, engagement, and conversion rates.
- Optimization: Media buying allows advertisers to optimise their campaigns based on real-time performance data, which enables them to make informed decisions and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Steps for Media Buying
Here are the typical steps involved in media buying:
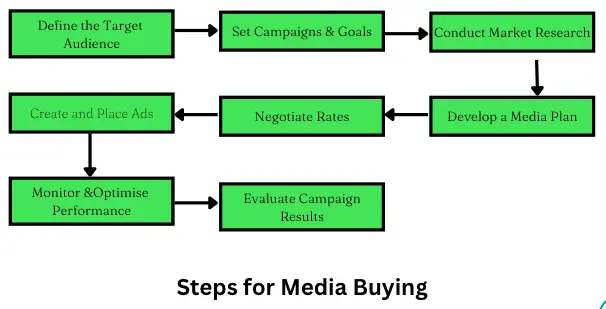
- Define the target audience: Determine the target audience for the advertising campaign, including their demographic, psychographic, and behavioural characteristics.
- Set campaign goals and objectives: Establish the goals and objectives of the advertising campaign, such as increasing brand awareness, generating leads, or driving sales.
- Conduct market research to identify the most influential media channels and ad placements for reaching the target audience based on audience reach, engagement, and cost.
- Develop a media plan: Develop a media plan that outlines the media channels, ad placements, and budgets for the advertising campaign.
- Negotiate rates and placements: Negotiate favourable rates and ad placements with media outlets based on the media plan and campaign goals.
- Create and place ads: Create the advertising content, such as copy, images, or videos, and place the ads on the selected media channels.
- Monitor and optimise performance: Monitor the performance of the advertising campaign using metrics such as reach, frequency, engagement, and conversion rates, and optimise the campaign based on real-time performance data.
- Evaluate campaign results: Evaluate the results of the advertising campaign against the established goals and objectives, and identify areas for improvement in future campaigns.
Future aspects of Media Buying
The future of media buying is likely to be shaped by several emerging trends and technologies, including:
- Data-driven targeting: Media buying increasingly relies on data-driven targeting techniques, such as programmatic advertising, that enable advertisers to reach the right audience with greater precision and efficiency.
- AI-powered automation: AI-powered automation will likely play a more significant role in media buying, enabling advertisers to automate tasks such as audience segmentation, ad placement, and performance optimization.
- Advanced analytics: Advanced analytics tools and techniques will likely become more prevalent in media buying, providing advertisers with deeper insights into campaign performance and audience behaviour.
- Cross-device targeting: As consumers increasingly use multiple devices to access content, media buying will likely shift towards cross-device targeting strategies that enable advertisers to reach consumers across various channels and devices.
- Privacy regulations: The growing importance of privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, will likely impact media buying by requiring advertisers to be more transparent about data collection and usage practices.
Example:
Coca-Cola has used various media channels and ad placements to reach its target audience, including television, print, digital, and outdoor advertising. Coca-Cola has also leveraged data-driven targeting techniques and programmatic advertising to reach its target audience more effectively and efficiently.

By carefully selecting the proper media channels and ad placements and monitoring performance metrics such as reach and engagement, Coca-Cola has successfully promoted its brand and products to consumers around the world.
FAQs
- What is media buying?
Media buying is advertising space or time across various media channels to reach a target audience and promote a brand, product, or service.
- Why is media buying necessary?
Media buying is important because it allows advertisers to reach their target audience effectively and efficiently. Advertisers can optimise their campaigns and achieve their advertising goals by selecting the proper media channels and ad placements and monitoring performance metrics.
- What are some common media channels used in media buying?
Common media channels used in media buying include television, radio, print, digital, and outdoor advertising.
- What is programmatic advertising?
Programmatic advertising is a data-driven approach to buying and selling advertising space that uses automated systems and algorithms to target specific audiences and optimise real-time ad placements.
- How do you measure the success of a media buying campaign?
The success of a media buying campaign can be measured using various performance metrics, such as reach, engagement, conversion rates, and return on investment (ROI).
- What is the role of data in media buying?
Data plays a critical role in media buying, enabling advertisers to target specific audiences with greater precision and efficiency. Advertisers can optimise their campaigns and achieve better results by leveraging data-driven targeting techniques and analytics tools.
- What are some emerging trends in media buying?
Emerging trends in media buying include data-driven targeting, programmatic advertising, AI-powered automation, advanced analytics, cross-device targeting, and privacy regulations.
Marketing Technology Roadmap
Definition
A marketing technology roadmap is a strategic plan that outlines the technology initiatives and projects necessary to achieve marketing goals and objectives.
Description
You need a roadmap for marketing to align marketing goals with technology initiatives, enabling organisations to prioritise investments and improve customer experiences. The structured outline provides a clear plan for implementing new technology and achieving business objectives, leading to greater efficiency and revenue growth.
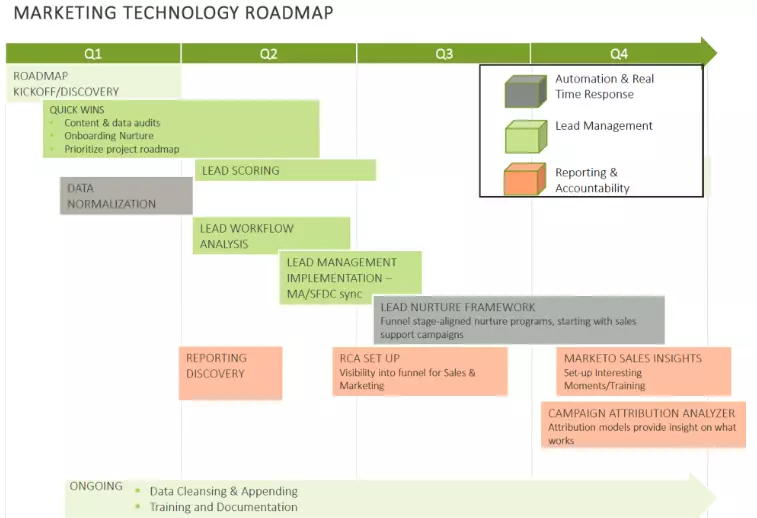
Source: www.demandgen.com
Marketing teams prioritise and plan their technology investments and deployments over a set period, usually several years.
The roadmap typically includes a detailed analysis of the existing marketing technology stack and identifies areas where technology can improve the customer experience, increase efficiency, and drive revenue growth.
By creating a marketing technology roadmap, organisations can align their marketing strategies with their technology capabilities, enabling them to stay competitive, meet customer needs, and achieve their business objectives.
Importance of Marketing Technology Roadmap
A marketing technology roadmap is essential for several reasons:
- Aligns marketing goals with technology initiatives: By creating a roadmap, organisations can ensure that their marketing strategies are supported by the right technology, enabling them to achieve their goals more efficiently.
- Prioritises technology investments: A roadmap helps to prioritise technology investments, ensuring that limited resources are directed towards the most impactful initiatives.
- Improves customer experiences: By identifying areas where technology can improve the customer experience, organisations can deliver better customer experiences and increase customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Enables revenue growth: A roadmap helps to identify technology initiatives that can drive revenue growth, such as marketing automation or personalization.
- Provides a clear implementation plan: The roadmap outlines the steps required to implement new technology, enabling organisations to plan and budget effectively and ensure successful deployment.
How to make a Marketing Technology Roadmap?
Here are the general steps to create a marketing technology roadmap:
- Define marketing goals: Identify the business objectives and goals the roadmap will support, such as increasing revenue, improving customer experiences, or optimising marketing operations.
- Assess current technology stack: Evaluate the existing marketing technology stack and identify areas where technology can be improved or optimised to better support marketing goals.
- Identify gaps: Identify technology gaps that must be filled to achieve marketing goals and prioritise them based on their impact and feasibility.
- Determine the budget: Estimate the budget required for each technology initiative and prioritise them based on the available resources and expected return on investment.
- Choose vendors: Research and select vendors or technology solutions that meet the requirements of each initiative.
- Plan implementation: Develop a detailed implementation plan for each technology initiative, including timelines, milestones, and resource requirements.
- Monitor and adjust: Monitor the implementation progress, measure the impact of the new technology on marketing goals, and adjust the roadmap as needed to ensure ongoing alignment with business objectives.
Future aspects of Marketing Technology Roadmap
The future of the marketing technology roadmap will likely include the following aspects:
- The increasing importance of AI and machine learning: AI and machine learning will become more prevalent in marketing technology stacks, enabling more advanced automation, personalization, and data analysis.
- The continued growth of marketing automation: Marketing automation will continue to grow, enabling marketing teams to automate repetitive tasks, improve efficiency, and deliver more personalised and relevant customer experiences.
- Greater emphasis on data privacy and security: With growing concerns over data privacy and security, marketing technology roadmaps must incorporate measures to protect customer data and comply with GDPR and CCPA.
- Integration of emerging technologies: Emerging technologies such as virtual reality, augmented reality, and voice assistants will become more integrated into marketing technology stacks, providing new opportunities for engaging and immersive customer experiences.
- Greater focus on omnichannel marketing: Marketing technology roadmaps must prioritise initiatives that support omnichannel marketing, enabling consistent and seamless experiences across all touchpoints.
Things to keep in mind while building Marketing Technology Roadmap
Here are some things to keep in mind while building a marketing technology roadmap:
- Focus on business objectives: Ensure that the marketing technology roadmap is aligned with the overall business objectives and marketing goals. The roadmap should support the organisation’s broader strategy and priorities.
- Involve stakeholders: Involve stakeholders from across the organisation in developing the marketing technology roadmap, including marketing, IT, sales, and customer service teams. This ensures buy-in and support for the roadmap’s initiatives.
- Prioritise initiatives: Prioritise the initiatives in the roadmap based on their impact and feasibility. Consider factors such as ROI, resource availability, and complexity when prioritising initiatives.
- Evaluate existing technology: Evaluate the existing marketing technology stack and identify areas where technology can be optimised or improved to better support marketing goals.
- Ensure scalability: Ensure that the technology initiatives in the roadmap are scalable and can support the organisation’s future growth and expansion.
- Consider integration: Consider how the new technology initiatives will integrate with existing systems and processes, and plan for integration and data migration accordingly.
- Develop a detailed implementation plan: Develop a clear plan for implementing each technology initiative, including timelines, milestones, and resource requirements. This helps ensure successful deployment and adoption.
Example:
Tata Motors is one of India’s largest automobile manufacturers. The brand’s marketing technology roadmap includes a plan to enhance the online presence. Tata Motors have invested in a more robust website and mobile app, including features such as a vehicle configurator, chatbot for customer support, and personalised content based on user behaviour.

The motor manufacturing leader, implements a marketing automation platform to automate and streamline marketing processes such as email marketing, social media advertising, and lead nurturing.
Tata Motors could use data analytics and machine learning to personalise the customer experience, such as recommending vehicles based on a customer’s previous interactions and preferences.
The motor brand creates virtual reality experiences to showcase their vehicles and provide immersive test drive experiences, enabling customers to experience the brand in a new way.
Tata Motors could leverage social media to engage with customers and build brand awareness, using tools such as social listening to understand customer sentiment and respond to feedback.
FAQs
What is a marketing technology roadmap?
A marketing technology roadmap is a strategic plan outlining how an organisation uses technology to achieve its marketing goals and objectives.
Why is a marketing technology roadmap essential?
A marketing technology roadmap is crucial because it helps organisations align technology initiatives with marketing goals, prioritise technology investments, and ensure ongoing optimization and alignment with business objectives.
What are some critical components of a marketing technology roadmap?
Some key components of a marketing technology roadmap include marketing goals and objectives, an assessment of the existing technology stack, identification of technology gaps, prioritisation of initiatives, a budget estimate, vendor selection, and a detailed implementation plan.
What are some future trends in the marketing technology roadmap?
Future trends in the marketing technology roadmap include increasing use of AI and machine learning, the continued growth of marketing automation, greater emphasis on data privacy and security, integration of emerging technologies such as virtual reality, and greater focus on omnichannel marketing.
How can organisations ensure success when implementing a marketing technology roadmap?
Organisations can ensure success when implementing a marketing technology roadmap by focusing on business objectives, involving stakeholders, prioritising initiatives, evaluating existing technology, ensuring scalability, considering integration, and developing a detailed implementation plan.
Marketing Technology
Definition
Marketing technology is the use of technology to support marketing activities and processes.
Description
Marketing technology can help businesses streamline marketing processes, improve customer engagement, and gain valuable insights into campaign performance, ultimately driving sales and increasing profitability in a highly competitive marketplace.

Marketing technology supports marketing activities and processes using digital tools, software, and platforms. MarTech can include a range of technologies, such as customer relationship management (CRM) software, marketing automation tools, social media management platforms, data analytics software, and content management systems (CMS).
Importance of Marketing Technology
This is why marketing technology is important:
- Marketing technology helps businesses to automate repetitive marketing tasks, saving time and resources.
- Marketing technology enables marketers to collect and analyse data on customer behaviour, preferences, and interactions, providing valuable insights that can inform marketing strategy.
- Marketing technology supports creating and delivering personalised marketing messages and experiences, improving customer engagement and loyalty.
- Marketing technology allows businesses to optimise marketing campaigns in real-time, based on performance data, improving ROI.
- Marketing technology helps businesses to stay competitive in a rapidly evolving digital landscape by keeping pace with emerging trends and technologies.
What are the types of marketing technology?
There are numerous types of marketing technologies, including:
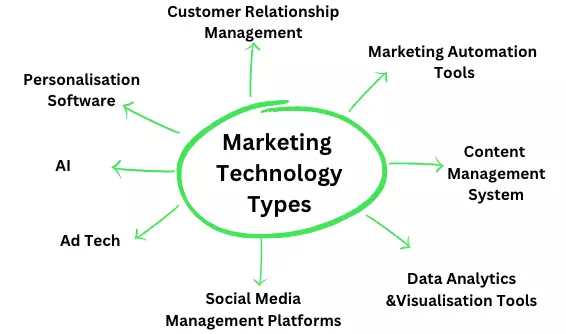
1. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software:
- The software is used to manage and analyse customer interactions and data throughout the lifecycle.
- CRM software helps businesses to centralise customer data, making it easier to analyse customer behaviour and preferences.
- By analysing customer data, CRM software can help businesses to better understand their target audience, enabling them to create more targeted and effective marketing campaigns.
- CRM software can also automate routine marketing tasks, such as lead nurturing and customer follow-up, allowing marketers to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- CRM software can help businesses track customer interactions across channels, providing a more seamless and personalised customer experience.
- CRM software can also provide insights into customer satisfaction and sentiment, enabling businesses to identify improvement areas and address customer concerns proactively.
- By providing a single view of the customer, CRM software can help businesses to improve customer retention and loyalty by enabling them to identify and respond to customer needs more effectively.
2. Marketing automation tools:
Used to automate repetitive marketing tasks such as email marketing, lead nurturing, and social media management.
- Streamlining processes: Marketing automation tools can automate repetitive marketing tasks such as email campaigns, social media management, and lead nurturing. This frees marketers to focus on more strategic initiatives and reduces the risk of errors or oversights.
- Targeting and personalization: Marketing automation tools can use customer data to personalise marketing messages and target them to specific audience segments. This can improve the effectiveness of marketing efforts by making them more relevant and engaging.
- Lead generation and nurturing: Marketing automation tools can help generate and nurture leads through automated workflows that deliver relevant content and communications based on customer behaviour and interests.
- Analytics and insights: Marketing automation tools can provide insights into customer behaviour, campaign performance, and other metrics, enabling marketers to make data-driven decisions and optimise campaigns in real time.
- Improved collaboration: Marketing automation tools can improve collaboration between marketing and sales teams by providing a single source of truth for customer data and automating lead handoffs and other processes.
3. Content Management Systems (CMS):
Used to create, manage, and publish digital content such as blogs, videos, and social media posts.
- Easy content creation and publishing: CMS platforms provide an easy-to-use interface for creating, editing, and publishing content, including blog posts, videos, and social media updates. This streamlines content creation and enables marketers to publish more quickly and efficiently.
- Search engine optimization (SEO): CMS platforms often include built-in SEO tools, such as meta tags and descriptions, that can help improve the visibility and ranking of content in search engine results pages (SERPs).
- Personalization and targeting: CMS platforms can enable businesses to create personalised content and target it to specific segments of their audience based on their interests and behaviour.
- Analytics and insights: CMS platforms often provide analytics and insights into content performance, including metrics such as page views, engagement, and conversions. This data can help marketers to optimise their content strategy and improve campaign performance.
- Collaboration: CMS platforms can facilitate cooperation between marketing and other teams, such as design and development, by providing a centralised content creation and management platform.
4. Data analytics and visualisation tools:
Used to collect, analyse, and visualise marketing data, enabling marketers to gain insights into campaign performance and customer behaviour. Some of the tools for data analytics and visualisation are Tableau, Google Data Studio, Domo, SAP Analytics Clouds, etc. The tools can help you in:
-
- Improved data insights: Data visualisation tools can help marketers to make sense of complex data sets and gain insights into customer behaviour, campaign performance, and other metrics. This can enable them to make data-driven decisions and optimise campaigns in real time.
- Better targeting: Data visualisation tools can enable marketers to segment their audience based on demographics, behaviour, and interests. This can help them to create more targeted and personalised marketing campaigns that are more likely to resonate with their audience.
- Improved communication: Data visualisation tools can help marketers to communicate complex data insights more effectively to stakeholders, including executives and other teams. This helps build buy-in for marketing initiatives and drives greater collaboration across the organisation.
- Enhanced performance tracking: Data visualisation tools can help marketers to track the performance of their campaigns in real time, including metrics such as website traffic, engagement, and conversions. This can enable them to identify areas for improvement and optimise campaigns for better results.
5. Social media management platforms:
Used to manage and analyse social media accounts and to engage with customers on social media platforms. Some of the social media management platforms you can rely on are Hootsuite, Sprout Social, Buffer, etc.
-
- Streamlined social media management: Platforms enable businesses to manage multiple social media accounts from a single dashboard. This can streamline social media management and save time.
- Content planning and scheduling: Social media management platforms provide businesses with tools to plan and schedule content in advance. This can help businesses create a consistent posting schedule and ensure their content is posted at the optimal times for their audience.
- Advanced targeting and segmentation: Social media management platforms provide businesses with advanced targeting and segmentation options, enabling them to create more targeted and effective social media campaigns.
- Social listening and monitoring: Social media management platforms provide businesses with tools to monitor social media conversations and track brand mentions. This can help businesses to stay on top of customer feedback and respond to comments promptly.
- Analytics and reporting: Social media management platforms provide businesses with access to analytics and reporting tools, enabling them to track the performance of their social media campaigns and make data-driven decisions to improve their marketing efforts.
6. Adtech:
Refers to a range of technologies used to manage and optimise digital advertising campaigns, such as programmatic advertising, retargeting, and ad networks.
Adtech platforms help marketing efforts by enabling businesses to create and deliver targeted advertising campaigns across various channels. Adtech platforms provide advanced targeting and segmentation options, allowing businesses to create highly relevant ads for their target audience. These platforms also provide businesses with real-time analytics and reporting, enabling them to track the performance of their ads and make data-driven decisions to optimise their campaigns.
Some of how ad tech platforms can help in marketing efforts include:
- Targeted advertising: Adtech platforms provide businesses with advanced targeting and segmentation options, allowing them to deliver highly targeted advertising campaigns to specific audiences.
- Real-time bidding: Adtech platforms enable businesses to bid in real-time for ad inventory, allowing them to optimise their ad spend and target the most relevant audiences at the right time.
- Programmatic advertising: Adtech platforms use programmatic advertising technology to automate ad-buying, enabling businesses to deliver ads at scale and optimise their campaigns in real time.
- Analytics and reporting: Adtech platforms provide businesses with access to real-time analytics and reporting, enabling them to track the performance of their campaigns and make data-driven decisions to improve their marketing efforts.
7. Personalization software:
These software creates and delivers personalised marketing messages and experiences based on customer data and behaviour.
-
- Improved customer experience: Personalization software enables businesses to deliver personalised content, recommendations, and offers to their customers, creating a more relevant and engaging customer experience.
- Increased customer engagement: Personalization software can help businesses increase customer engagement by delivering personalised content and offers more likely to resonate with their target audience.
- Higher conversion rates: By delivering personalised content and offers, businesses can increase the likelihood of conversion and ultimately drive more revenue.
- Improved customer loyalty: Personalization software can help businesses build stronger relationships with their customers by delivering personalised experiences that demonstrate an understanding of their needs and preferences.
- Data-driven insights: Personalization software generates valuable data and insights businesses can use to refine their marketing strategies and improve their overall performance.
8. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) tools:
Used to automate and optimise marketing processes, such as content creation, email marketing, and customer service.
-
- Personalization: AI and ML can analyse vast amounts of customer data to create personalised content and experiences more likely to engage and convert customers.
- Predictive analytics: AI and ML can predict customer behaviour and preferences based on historical data, allowing businesses to anticipate customer needs and make data-driven decisions to improve their marketing efforts.
- Automation: AI and ML can automate repetitive tasks such as lead scoring, email marketing, and social media management, freeing marketers to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Optimization: AI and ML can analyse and optimise marketing campaigns in real time, identifying patterns and insights that can be used to improve targeting, messaging, and overall performance.
- Customer service: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can provide customers quick and efficient support, improving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Future Aspect of Marketing Technology
- Increased use of artificial intelligence and machine learning in marketing technology
- Greater integration and automation across different marketing channels and platforms
- Continued focus on personalization and customer experience
- Use of data analytics and visualisation tools to gain insights into customer behaviour and preferences
- The emergence of new technologies, such as virtual and augmented reality for immersive experiences and innovative customer engagement
- Ongoing innovation and evolution to stay ahead of the curve and deliver more effective personalised marketing.
Example:
Flipkart is an e-commerce company that has used various marketing technologies to enhance its online shopping experience, increase customer engagement, and boost sales. Some marketing technologies Flipkart uses include Personalization software to create customised product recommendations, tailored promotions and personalised content based on customers’ browsing and purchase history.

The company also uses CRM software to manage customer data, track interactions, and provide personalised customer support. Flipkart uses social media management tools to manage its social media accounts, engage with customers, and monitor online conversations about its brand.
Flipkart uses various ad tech platforms to target and retarget customers with personalised ads, increase brand awareness, and drive sales.
FAQs
What is marketing technology?
Marketing technology refers to businesses’ various tools, software, and platforms to manage, automate, and analyse their marketing efforts.
Why is marketing technology important?
Marketing technology is important because it enables businesses to streamline their marketing processes, increase efficiency and productivity, and gain valuable insights and analytics to refine their marketing strategies.
What are some examples of marketing technology?
Some examples of marketing technology include customer relationship management (CRM) software, marketing automation tools, content management systems (CMS), data analytics and visualisation tools, social media platforms, ad tech platforms, personalization software, and artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML) tools.
How can CRM software help improve marketing efforts?
CRM software can help improve marketing efforts by centralising customer data, providing insights and analytics on customer behaviour and preferences, automating lead management and sales processes, and providing personalised customer support.
How can marketing automation tools help improve marketing efforts?
Marketing automation tools can help improve marketing efforts by automating repetitive tasks such as email marketing, lead scoring, and social media management, allowing marketers to focus on more strategic initiatives.
How can social media platforms and management tools help improve marketing efforts?
Social media platforms and management tools can help improve marketing efforts by allowing businesses to engage with customers, monitor online conversations about their brand, and create targeted and personalised social media campaigns.
How can AI/ML tools help improve marketing efforts?
AI/ML tools can help improve marketing efforts by providing personalised content and experiences, predicting customer behaviour and preferences, automating repetitive tasks, optimising marketing campaigns, and providing valuable insights and analytics to refine marketing strategies.
How can businesses choose the right marketing technology for their needs?
Businesses can choose the right marketing technology for their requirements by identifying their specific goals and pain points, evaluating the features and capabilities of different technologies, and considering factors such as ease of use, scalability, and cost. It’s also important to stay up-to-date on emerging trends and technologies in the marketing technology landscape.
Marketing Strategy
Definition
A marketing strategy refers to a company’s overall plan for promoting and selling its products or services by understanding customer’s needs.
Description
Marketing strategy helps companies promote and sell their products or services by identifying target markets, defining unique value propositions, and developing tactics to engage potential customers.

It involves identifying target markets, understanding customer needs and preferences, defining the company’s unique value proposition, and developing tactics to reach and engage potential customers.
A marketing strategy may include advertising, public relations, sales promotions, and other tactics to build brand awareness, generate leads, and drive sales. In addition, a marketing strategy aims to create a sustainable competitive advantage for the company in its chosen market.
Importance of Marketing Strategy
Marketing strategy is essential because it helps companies to:
- Identify and understand their target markets, which allows them to tailor their products and services to meet customer needs and preferences.
- Develop a unique value proposition that sets the brand apart from competitors and creates a competitive advantage that can drive sales and profitability over the long term.
How to make a Marketing Strategy?
Developing a marketing strategy typically involves the following steps:
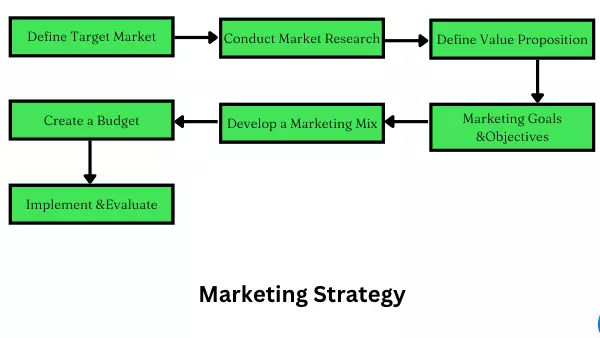
- Define your target market: Identify your ideal customer and determine their needs, wants, and preferences.
- Conduct market research: Gather information about your target market, competitors, industry trends, and other relevant factors that may impact your business.
- Define your unique value proposition: Determine what sets your product or service apart from others in the market and articulate it clearly.
- Set marketing goals and objectives: Define specific, measurable goals that align with your business objectives.
- Develop a marketing mix: Determine which tactics (e.g. advertising, public relations, social media, etc.) you will use to reach your target market and achieve your marketing goals.
- Create a budget: Allocate resources (e.g. time, money, staff) to support your marketing activities.
- Implement and evaluate: Execute your marketing plan and monitor its performance, making necessary adjustments to meet your goals and objectives.
Types of Marketing Strategies
There are several types of marketing strategies that companies can use, including:
- Digital marketing: Leveraging online channels such as social media, email, and search engines to promote products or services.
- Content marketing: Creating and distributing valuable, relevant content to attract and retain a target audience.
- Relationship marketing focuses on building long-term customer relationships by providing exceptional customer service and personalised experiences.
- Influencer marketing: Collaborating with social media influencers to promote products or services to their followers.
- Guerrilla marketing: Using unconventional tactics, such as stunts or flash mobs, to create buzz and generate attention for a brand.
- Product differentiation: Emphasising unique features or benefits of a product or service to distinguish it from competitors.
- Price differentiation: Offering different pricing options or discounts to appeal to customer segments.
- Segmentation and targeting: Identifying specific customer groups and tailoring marketing messages to their needs and preferences.
- Branding: Creating a distinct brand identity through visual and messaging elements to build recognition and loyalty.
Future Aspect of Marketing Strategy for Online Marketing
The future of marketing strategy for online marketing is likely to involve several key trends:
- Personalization: As technology advances, marketers can create more personalised customer experiences, using data to deliver tailored content, recommendations, and offers.
- AI and automation: Artificial intelligence and automation will increasingly streamline marketing processes, improve targeting, and provide more efficient customer service.
- Voice search optimization: With the growing popularity of voice-activated assistants like Siri and Alexa, marketers must optimise their content for voice search queries.
- Interactive content: Interactive content such as quizzes, polls, and augmented reality experiences will become more common, offering engaging and immersive ways to promote products and services.
- Video marketing: Video content will continue to be a powerful marketing tool, with live video, 360-degree video, and virtual reality experiences becoming more prevalent.
- Omnichannel marketing: As customers interact with brands across multiple channels, marketers must create seamless experiences integrating online and offline touchpoints.
Read More : All About Content Creation, Curation & Distribution For a Winning Marketing Strategy
Example:
Netflix’s marketing strategy is focused on creating a strong brand identity and delivering personalised content to its target audience. Some critical elements of its strategy include:
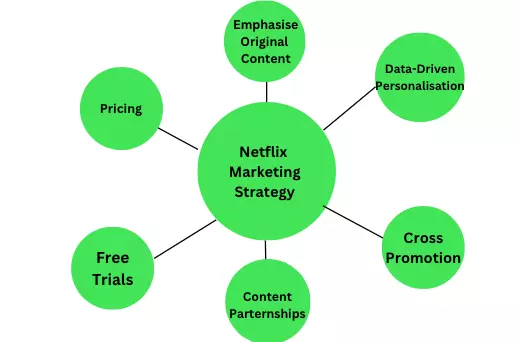
- Emphasising original content: Netflix has invested heavily in producing original movies and TV shows, which helps to differentiate its offering and build customer loyalty. Stranger Things, Virgin River, The Crown, etc are some of the examples which have stolen the viewers mind and helped Netflix earn their large share in the market.
- Data-driven personalization: Using data and algorithms to suggest content based on a customer’s viewing history and preferences helps keep them engaged and reduces churn. The predictions by Netflix shows 80% accurate suggestions in what the users might be interested in.
- Cross-promotion: Promoting new releases to customers through email, social media, and in-app notifications, which helps to drive viewership and boost engagement.
- Content partnerships: Partnering with studios and other content providers to licence popular movies and TV shows helps fill gaps in its content library and attract new customers.
- Free trials and pricing: Offering free trials and flexible pricing options to attract new customers and retain existing ones.
FAQs
What is a marketing strategy?
A marketing strategy is a plan that outlines how a company will promote and sell its products or services to target customers. It involves identifying target markets, developing unique value propositions, and creating tactics to engage potential customers.
Why is marketing strategy necessary?
Marketing strategy is essential because it helps companies to identify and understand their target markets, develop a unique value proposition, and create a competitive advantage that can drive sales and profitability over the long term.
What are the steps involved in making a marketing strategy?
The steps in making a marketing strategy include defining your target market, conducting market research, defining your unique value proposition, setting marketing goals and objectives, developing a marketing mix, creating a budget, and implementing and evaluating your plan.
What are the different types of marketing strategies?
There are several marketing strategies, including digital marketing, content marketing, relationship marketing, influencer marketing, guerrilla marketing, product differentiation, price differentiation, segmentation and targeting, and branding.
What are the future aspects of marketing strategy for online marketing?
The future of marketing strategy for online marketing is likely to involve personalization, AI and automation, voice search optimization, interactive content, video marketing, and omnichannel marketing.
What is the marketing strategy of Netflix?
The marketing strategy of Netflix is centred on delivering a personalised and convenient viewing experience to its target audience while investing in original content to differentiate itself from competitors. Key elements of its strategy include emphasising original content, data-driven personalization, cross-promotion, content partnerships, and flexible pricing options.
Marketing Planning
Definition
Marketing planning is the process of creating a roadmap for achieving marketing goals and objectives through the use of various marketing strategies and tactics.
Description
Marketing planning is necessary for businesses to achieve their goals and objectives by creating a roadmap for implementing effective marketing strategies and tactics. It helps businesses to analyse the market, identify the target audience, allocate resources efficiently, and evaluate the success of their marketing campaigns.

Importance of Marketing Planning
Marketing planning is essential for businesses of all sizes and industries. Here are some reasons why marketing planning is essential:
- Sets clear goals and objectives: Marketing planning helps businesses to set clear and measurable goals and objectives. This provides direction and focuses for the marketing activities and ensures that efforts are aligned with overall business objectives.
- Identifies target audience: Marketing planning helps businesses to identify and understand their target audience. This allows them to tailor their marketing strategies and tactics to the audience’s specific needs and preferences, improving the marketing campaign’s effectiveness.
- Allocates resources efficiently: Marketing planning helps businesses to allocate their resources, including time, money, and personnel, efficiently. This ensures that resources are used effectively and efficiently to achieve marketing goals and objectives.
- Improves decision-making: Marketing planning provides businesses with a better understanding of the market and competitor activity. This allows them to make informed decisions about marketing strategies and tactics, increasing their chances of success.
- Facilitates evaluation and improvement: Marketing planning helps businesses evaluate their marketing campaigns’ success. This allows them to identify areas for improvement and make changes to future campaigns to improve their effectiveness.
Steps to follow for Marketing Planning
Let us read the steps in marketing planning:
- The first step in marketing planning is market analysis. This involves researching the market to identify trends, consumer behaviour, and competitor activity. This information is used to better understand the target audience, their needs and preferences, and the overall market landscape.
- The next step is to identify the target audience. This involves defining the demographics, psychographics, and behaviour of the audience that the marketing campaign is aimed at. Understanding the target audience is crucial for developing marketing strategies that resonate with them.
- Once the target audience has been identified, the marketing strategies can be developed. This involves deciding on the marketing mix, which includes product, price, promotion, and place. The marketing mix is tailored to the target audience and designed to achieve the marketing goals and objectives.
- After the marketing strategies have been developed, a budget can be created. This involves estimating the costs associated with the marketing campaign and allocating resources accordingly. The budget is an important part of marketing planning, ensuring that the campaign is financially viable and that resources are used efficiently.
- Once the budget has been finalised, the marketing campaign can be implemented. This involves creating and executing marketing strategies, including advertising, public relations, social media, and other promotional activities. It is important to monitor the campaign’s performance and make adjustments as needed to ensure that it achieves the desired results.
- Finally, the marketing campaign should be evaluated to determine its success. This involves analysing and comparing the campaign results to the marketing goals and objectives. If the campaign is successful, the strategies and tactics used can be replicated in future campaigns. Conversely, if the campaign is not successful, adjustments can be made to improve future campaigns.
Tools for Marketing Planning
There are various tools that businesses can use for marketing planning. Here are some examples:
- SWOT analysis: SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool that helps businesses to identify their Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. This analysis can be used to inform marketing strategies and tactics.
- Market research: Market research involves gathering and analysing data about the market, including consumer behaviour, trends, and competitor activity. This information can be used to develop effective marketing strategies and tactics.
- Customer persona development: Developing customer personas involves creating ideal customer profiles based on demographics, psychographics, and behaviour. This information can be used to tailor marketing strategies and tactics to the specific needs and preferences of the target audience.
- Marketing mix: The marketing mix includes product, price, promotion, and place. It is a tool that businesses can use to develop a comprehensive marketing strategy that considers all aspects of the marketing campaign.
- Budgeting tools: Budgeting tools, such as spreadsheets or software, can estimate the costs associated with the marketing campaign and allocate resources efficiently.
- Marketing automation: Marketing automation tools can automate various marketing tasks, such as email campaigns, social media posting, and lead generation. This can save time and improve the efficiency of the marketing campaign.
- Metrics and analytics: Metrics and analytics tools can be used to track the marketing campaign’s performance and evaluate its effectiveness. This information can be used to make adjustments and improvements to future campaigns.
Example:
One example of a brand that has implemented effective marketing planning is Coca-Cola. As a result, Coca-Cola’s long history of successful marketing campaigns has consistently remained one of the world’s most valuable brands.
One of the critical aspects of Coca-Cola’s marketing planning is its focus on understanding and connecting with its target audience. Through extensive market research and customer profiling, Coca-Cola has identified its target audience as young people aged 18-34 looking for refreshing and fun experiences.
Based on this understanding, Coca-Cola has developed a comprehensive marketing mix that includes a variety of advertising campaigns, sponsorships, and promotions that appeal to this target audience. For example, Coca-Cola’s “Share a Coke” campaign encouraged customers to purchase personalised bottles of Coca-Cola with their own names or the names of their friends, which created a sense of personalization and social sharing.
Coca-Cola also uses social media and digital marketing to connect with its audience and create engaging content that aligns with its brand values. For example, the company’s “Taste the Feeling” campaign features emotionally-driven advertisements focusing on the experience and enjoyment of drinking Coca-Cola rather than the product itself.
FAQs
What is marketing planning?
Marketing planning is developing a structured approach for implementing effective marketing strategies and tactics to help businesses achieve their goals and objectives.
Why is marketing planning important?
Marketing planning is important because it helps businesses set clear goals and objectives, identify the target audience, allocate resources efficiently, improve decision-making, and facilitate evaluation and improvement of marketing campaigns.
What are the critical components of marketing planning?
The critical components of marketing planning include market research, customer analysis, target audience identification, marketing mix development, budgeting, and evaluation and measurement.
How can businesses use marketing planning to improve their ROI?
Businesses can use it to improve their ROI by focusing on the most effective marketing strategies and tactics aligned with their goals and objectives and operating metrics and analytics to track the performance of their campaigns and make adjustments accordingly.
How often should businesses update their marketing plans?
Marketing plans should be updated regularly to ensure they remain relevant and practical. The frequency of updates will depend on the industry, market conditions, and business goals and objectives.
What are some common challenges in marketing planning?
Some common challenges include a need for more resources, insufficient data, changing market conditions, and difficulty accurately predicting consumer behaviour.
How can businesses overcome these challenges in marketing planning?
Businesses can overcome these challenges by investing in market research, prioritising and allocating resources effectively, using predictive analytics to forecast consumer behaviour, and remaining flexible and adaptable in response to changing market conditions.
Marketing Operations
Definition
Marketing operations can be defined as optimising, streamlining, and managing an organisation’s various marketing activities and processes to improve efficiency, effectiveness, and alignment with business goals.
Description
Businesses can leverage technology, data, and analytics to optimise marketing strategies and tactics to increase efficiency and improve marketing effectiveness.

Marketing operations typically involve budget management, project management, campaign planning and execution, data analysis, performance measurement, and reporting. It also includes developing and maintaining marketing technology systems, such as customer relationship management (CRM) platforms, marketing automation software, and analytics tools.
Marketing operations aim to ensure that marketing efforts are aligned with overall business objectives, and to help marketing teams achieve their goals cost-effectively and efficiently. By leveraging data and technology, marketing operations can help organisations improve their targeting, segmentation, and personalization efforts, ultimately driving better results and ROI from their marketing initiatives.
Importance of Marketing Operations
Marketing operations are crucial for organisations that want to maximise the impact and ROI of their marketing efforts. Here are some reasons why marketing operations is important:
- Efficiency: Marketing operations helps improve the efficiency of marketing processes by streamlining workflows, automating repetitive tasks, and reducing manual efforts. This enables marketing teams to focus on higher-value activities such as strategy development and creative execution.
- Alignment: Marketing operations helps ensure marketing efforts align with overall business goals and objectives. By providing a framework for planning and execution, marketing operations helps teams stay focused on the most important initiatives and ensures that resources are allocated appropriately.
- Data-driven decision making: Marketing operations leverages data and analytics to inform decision making, enabling teams to make informed choices based on real-time data and insights. This helps teams optimise their campaigns, improve targeting and segmentation, and measure the effectiveness of their efforts.
- Consistency: Marketing operations helps ensure consistency across all marketing channels and initiatives, ensuring that messaging, branding, and creative are consistent across all touchpoints. This helps build brand equity and fosters a cohesive customer experience.
- Scalability: Marketing operations helps organisations scale their marketing efforts as they grow, enabling them to expand their reach and target new audiences while maintaining the same level of efficiency and effectiveness.
How to Make a Marketing Operations Strategy?
Developing a marketing operations strategy involves a series of steps that help to ensure that your marketing efforts are aligned with overall business objectives, and that you have a clear roadmap for achieving your goals. Here are some steps to consider when developing a marketing operations strategy:
- Define your goals and objectives: Before developing a marketing operations strategy, it’s important to define
your goals and objectives. What do you want to achieve with your marketing efforts? Are you looking to increase brand awareness, drive lead generation, or improve customer retention? Understanding your goals and objectives will help to guide your strategy and ensure that your efforts are aligned with business objectives. - Assess your current marketing operations: Once you have defined your goals and objectives, you must assess your current marketing operations. This involves evaluating your existing marketing processes, systems, and tools to identify areas of improvement. This step is critical to understanding where you stand and where you need to go.
- Identify key areas for improvement: Based on your assessment, identify the key areas for improvement. This could include streamlining workflows, improving data management, increasing automation, enhancing reporting and analysis capabilities, or other areas needing improvement.
- Develop a roadmap: Develop a roadmap that outlines the steps you need to take to achieve your goals and improve your marketing operations. This roadmap should include specific actions, timelines, and responsibilities.
- Implement changes: Once you have developed your roadmap, it’s time to implement the necessary changes. This may involve investing in new marketing technology, developing new processes, or training your team on new systems and workflows.
- Measure and optimise: After implementing changes, it’s important to measure the effectiveness of your marketing operations strategy and optimise as necessary. This involves monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) and using data and analytics to continuously improve your marketing efforts.
Future Strategies of Marketing Operations
Marketing operations are constantly evolving as new technologies, trends, and customer behaviours emerge. Here are some future strategies that may shape the direction of marketing operations:
- Personalization: As customers increasingly expect personalised experiences, marketing operations must prioritise personalization strategies. This could include leveraging data and analytics to better understand customer preferences and behaviour, and using technology to deliver customised experiences across all touchpoints.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning: As AI and machine learning continue to advance, marketing operations will increasingly rely on these technologies to automate tasks, analyse data, and optimise campaigns. This could include using AI-powered chatbots for customer service, or leveraging machine learning algorithms to improve targeting and segmentation efforts.
- Data privacy and security: With growing concerns around data privacy and security, marketing operations must prioritize strategies that protect customer data and ensure compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA. This could include implementing data encryption, conducting regular audits, and ensuring all third-party vendors comply with relevant regulations.
- Omnichannel marketing: As customers increasingly interact with brands across multiple channels and devices, marketing operations must prioritize strategies that enable seamless omnichannel experiences. This could include developing integrated marketing campaigns that leverage multiple channels, or investing in technologies that enable real-time personalization across all touchpoints.
- Agile marketing: As the pace of business continues to accelerate, marketing operations will need to adopt agile methodologies that enable faster, more iterative campaign development and execution. This could include using agile project management tools, developing cross-functional teams, and adopting a test-and-learn approach to marketing.
Example:
Zomato, a food delivery and restaurant discovery platform follows this marketing operations strategy:
- Data-driven decision making: Zomato uses data and analytics to inform its marketing strategies, allowing the company to make informed decisions based on real-time insights. For example, the company leverages customer data to personalise its marketing campaigns and improve targeting and segmentation efforts.
- Focus on customer experience: Zomato prioritises the customer experience across all touchpoints, from the app and website to customer service interactions. The company uses customer feedback to continuously improve its products and services, and invests in technologies that enable seamless customer experiences.
- Integration of marketing channels: Zomato uses an integrated marketing approach, leveraging multiple channels such as email, social media, and SMS to engage with customers and drive conversions. The company also invests in content marketing, using blog posts, videos, and other content formats to educate and engage customers.
- Emphasis on innovation: Zomato prioritises innovation in its marketing operations, investing in new technologies and strategies to stay ahead of the curve. For example, the company has experimented with augmented reality features in its app, allowing customers to see restaurant menus in 3D.
- Localization: Zomato has customised its marketing strategies for the Indian market, recognizing the importance of localization in driving engagement and conversions. For example, the company has launched region-specific marketing campaigns highlighting local cuisine and cultural events.
FAQs
What are marketing operations?
Marketing operations refers to the processes and strategies that support the planning, execution, and measurement of marketing campaigns and initiatives.
What are the key components of marketing operations?
The critical components of marketing operations include strategy development, campaign planning and execution, project management, budgeting and financial management, data management and analytics, and technology and infrastructure management.
What are the benefits of marketing operations?
Marketing operations can help organisations streamline their marketing processes, improve collaboration and communication between marketing teams and other departments, ensure consistency and quality across marketing campaigns, and optimise marketing performance through data-driven decision-making.
What technologies are used in marketing operations?
Technologies used in marketing operations can include marketing automation platforms, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, project management tools, data analytics platforms, and content management systems (CMS).
How can marketing operations improve customer experiences?
Marketing operations can improve customer experiences by ensuring that marketing campaigns and initiatives are aligned with customer needs and preferences, delivering personalised experiences across all touchpoints, and optimising customer journeys through data-driven insights and optimizations.
What skills are required for a career in marketing operations?
Skills required for a career in marketing operations can include project management, data analysis, technology management, financial management, communication and collaboration, and strategic thinking.
What is the future of marketing operations?
The future of marketing operations will likely be shaped by emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, a focus on personalization and customer experience, data privacy and security, omnichannel marketing, and agile methodologies.
Marketing Intelligence
Definition
Marketing intelligence is the process of gathering and analysing data related to a company’s market, customers, and competitors to inform strategic decision-making.
Description
Marketing intelligence collects, analyses, and interprets data related to a company’s market, customers, and competitors to inform strategic decision-making. It involves gathering primary and secondary data from various sources, including market research, customer feedback, and competitor analysis.
The primary purpose of marketing intelligence is to help companies better understand their target market and their competitors and identify new opportunities for growth and innovation. By gathering and analysing customer behaviour, preferences, and trends, companies can develop more targeted marketing strategies and improve their overall customer experience.
Marketing intelligence can also help companies identify potential threats to their business, such as new competitors or changes in consumer behaviour, and develop proactive strategies to mitigate those risks. It can also inform product development and innovation by providing insights into customer needs and preferences.
Some standard techniques used in marketing intelligence include surveys, focus groups, customer feedback, social media listening, website analytics, and competitor analysis. Data is often collected and analysed using specialised software and tools, such as data visualisation software, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, and business intelligence (BI) platforms.
Importance of Marketing Intelligence
Marketing intelligence is crucial for businesses because it enables them to make informed decisions based on data and insights rather than guesswork or assumptions. Here are some of the key reasons why marketing intelligence is essential:
- A better understanding of customers: By gathering and analysing customer behaviour, preferences, and trends, companies can develop a deeper understanding of their target market and create more targeted and effective marketing strategies.
- Improved competitive positioning: Marketing intelligence helps companies monitor their competitors and stay up-to-date on industry trends, enabling them to identify opportunities for differentiation and maintain a competitive edge.
- Enhanced product development: By gathering customer feedback and analysing market trends, companies can develop products that better meet customer needs and preferences.
- Increased ROI: Marketing intelligence enables companies to optimise their marketing strategies, targeting the right audience with the right message at the right time, which can lead to increased sales and ROI.
- Proactive risk management: Marketing intelligence helps companies identify potential threats to their business, such as new competitors or changes in consumer behaviour, and develop proactive strategies to mitigate those risks.
How to optimise Marketing Intelligence?
Optimising marketing intelligence involves several key steps:
- Define clear objectives: Start by defining goals for your marketing intelligence efforts. What do you hope to achieve? What questions do you need to answer? This will help you stay focused and ensure you collect and analyse the correct data.
- Collect the correct data: Identify the data sources to collect the information required to achieve your objectives. This may include primary research, such as surveys and focus groups, and secondary research, such as industry reports and social media monitoring.
- Analyze and interpret the data: Once you have collected the data, you need to analyze and analyze it to gain insights. This may involve data visualization tools, statistical analysis, or other techniques to uncover patterns and trends.
- Share insights: Share the insights you have gained with relevant stakeholders, such as marketing teams, product development teams, or senior executives. This will help ensure the senses inform decision-making and drive results.
- Take action: Use the insights gained through marketing intelligence to make data-driven decisions and optimize your marketing efforts. This may involve adjusting your marketing strategy, targeting specific customer segments, or developing new products.
- Continuously monitor and refine: Marketing intelligence is an ongoing process, so it’s essential to constantly monitor and refine your efforts based on new data and insights. Regularly review your objectives and data sources to ensure you collect the correct information to drive results.
Future Aspect of Marketing Intelligence
The future of marketing intelligence is expected to be shaped by several key trends:
- Artificial intelligence (AI): AI is already being used to automate tasks such as data collection and analysis, and it is expected to become more prevalent in marketing intelligence. AI can help marketers make sense of large volumes of data and identify patterns and insights that would be difficult to uncover manually.
- Predictive analytics: Predictive analytics uses data, statistical algorithms, and machine learning techniques to identify the likelihood of future outcomes based on historical data. As marketers seek to become more data-driven and proactive, predictive analytics is expected to become more critical in marketing intelligence.
- Real-time data analysis: The ability to analyse data in real time is becoming increasingly important as marketers seek to respond quickly to changing market conditions and customer needs. Real-time data analysis allows marketers to make informed decisions in real-time rather than relying on historical data.
- Omnichannel marketing intelligence: As consumers increasingly use multiple channels to interact with brands, marketing intelligence must incorporate data from various channels, including social media, mobile apps, email, and more.
- Privacy and data security: As data privacy and security concerns continue to grow, marketers must ensure that their marketing intelligence efforts comply with relevant regulations and best practices.
Example:
One example of marketing intelligence in India is using digital analytics to gather insights into consumer behaviour and preferences. Companies in India can collect data on website traffic, social media engagement, and search engine queries to understand how their target audience interacts with their brand online.
This information can then be used to create targeted marketing campaigns, improve customer experience, and develop new products or services that better meet consumer needs. Additionally, companies in India can use market research and competitive analysis to stay up-to-date on industry trends and better understand their competitors.
By leveraging marketing intelligence, companies in India can make informed business decisions and remain competitive in their respective markets.
FAQs
What is marketing intelligence?
Marketing intelligence is collecting and analysing data to gain insights into consumer behaviour, market trends, and competitor activity. It helps businesses make informed decisions about marketing strategy, product development, and overall business operations.
What kind of data is used in marketing intelligence?
Marketing intelligence uses a variety of data sources, including consumer surveys, website analytics, social media data, sales figures, and industry reports. The goal is to collect as much data as possible to comprehensively understand the market and consumer behaviour.
How is marketing intelligence different from market research?
Market research gathers information about consumer needs, preferences, and behaviour. Marketing intelligence, on the other hand, goes beyond market research by analysing a more comprehensive range of data sources and providing insights into broader market trends and competitor activity.
How is marketing intelligence used in business?
Marketing intelligence informs marketing strategy, product development, and overall business operations. By analysing consumer behaviour, market trends, and competitor activity, businesses can make informed decisions about positioning their products, which marketing channels to use, and how to stay ahead of their competitors.
What are some examples of marketing intelligence tools?
Many marketing intelligence tools are available, including website analytics software, social media listening tools, and market research platforms. Some famous examples include Google Analytics, Hootsuite, and Mintel. Businesses can also work with marketing intelligence agencies to gather and analyse data on their behalf.
How can marketing intelligence help businesses stay competitive?
Businesses can make informed decisions about marketing strategy and product development by gathering insights into consumer behaviour, market trends, and competitor activity. This allows them to stay ahead of their competitors and better meet the needs of their target audience. Marketing intelligence also helps businesses identify opportunities for growth and expansion.
Marketing Cloud
Definition
A marketing cloud is a software platform providing businesses with a suite of marketing tools and services for managing and optimising their campaigns across multiple channels.
Description
A marketing cloud is a software platform that provides businesses with a suite of marketing tools and services for managing and optimising their marketing campaigns across multiple channels, such as email, social media, search, mobile, and display advertising.
Source: https://email.uplers.com/
Marketing clouds typically offer a range of features and functionalities, including:
- Data management: Marketing clouds can aggregate and analyse data from various sources, including customer profiles, transactional data, and web behaviour data, to gain insights into customer behaviour and preferences.
- Campaign management: Marketing clouds enable businesses to plan, create, and execute marketing campaigns across multiple channels, from email and social media to mobile and display advertising. This can include designing and sending emails, creating social media posts, and launching targeted advertising campaigns.
- Personalization: Marketing clouds allow businesses to create personalised marketing messages and customer experiences based on their preferences, behaviours, and past interactions with the brand.
- Analytics and reporting: Marketing clouds offer robust analytics and reporting capabilities, allowing businesses to track and measure the performance of their marketing campaigns across various channels and make data-driven decisions.
- Integration: Marketing clouds can integrate with other systems and technologies, such as customer relationship management (CRM) and sales automation tools, to provide a seamless and integrated marketing and sales experience.
Importance of Marketing Cloud
Marketing cloud platforms are becoming increasingly crucial for businesses because they provide comprehensive tools and services for managing and optimising marketing campaigns across multiple channels. Here are some key reasons why marketing clouds are essential:
- Improved efficiency: Marketing clouds can streamline and automate many aspects of the marketing process, such as campaign management, audience segmentation, and content creation, saving businesses time and resources.
- Enhanced customer insights: Marketing clouds enable businesses to gather and analyse data from various sources, including customer profiles and behavioural data, to gain insights into customers’ preferences, behaviours, and needs.
- Personalization: Marketing clouds allow businesses to create personalised marketing messages and customer experiences, improving engagement, loyalty, and retention.
- Better targeting: Marketing clouds offer sophisticated targeting capabilities, enabling businesses to reach the right audience with the right message at the right time, resulting in higher conversion rates and ROI.
- Multi-channel marketing: Marketing clouds support marketing campaigns across multiple channels, from email and social media to mobile and display advertising, ensuring that businesses can reach their customers wherever they are.
How to use Marketing Cloud?
You can use Marketing Cloud by following these steps:
- Set up the platform: The first step is to set up the marketing cloud platform by configuring user accounts, connecting data sources, and integrating with other systems and technologies.
- Define your marketing objectives: Before launching any marketing campaigns, it’s essential to define your marketing objectives, such as increasing brand awareness, generating leads, or driving sales.
- Segment your audience: Marketing clouds allow businesses to segment their audience based on various criteria, such as demographics, behaviour, and past interactions with the brand.
- Create marketing campaigns: Once you have defined your marketing objectives and segmented your audience, creating your marketing campaigns using the platform’s campaign management tools is time. This can include designing and sending emails, creating social media posts, and launching targeted advertising campaigns.
- Personalise your messaging: Marketing clouds allow businesses to create personalised marketing messages and experiences for their customers based on their preferences, behaviours, and past interactions with the brand.
- Monitor and measure performance: It’s essential to monitor and measure the performance of your marketing campaigns across various channels using the platform’s analytics and reporting tools. This can help you identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions.
- Optimise your campaigns: Based on your performance data, you can optimise your campaigns by adjusting your messaging, targeting, and channel mix to improve your results.
Future Aspects of Marketing Cloud
The future of marketing cloud platforms is likely to involve several key developments, including:
- Greater integration with AI and machine learning: Marketing clouds will increasingly incorporate AI and machine learning capabilities to help businesses automate and optimise their marketing efforts, from personalised messaging to predictive analytics.
- More emphasis on customer data privacy and security: As concerns over data privacy and security continue to grow, marketing clouds must prioritise these issues and provide robust security measures to protect customer data.
- Increasingly sophisticated personalization capabilities: Marketing clouds will continue to improve their personalization capabilities, leveraging data and AI to create highly targeted and personalised customer marketing experiences.
- Expansion of marketing channels: Marketing clouds will continue to expand their capabilities to cover more marketing channels, such as messaging apps and voice assistants, to enable businesses to reach customers wherever they are.
- More seamless integration with other systems and technologies: Marketing clouds will become increasingly integrated with other systems and technologies, such as customer relationship management (CRM) and e-commerce platforms, to provide a more holistic view of the customer journey.
Features of Marketing Cloud
Marketing cloud platforms typically offer a range of features to help businesses manage their marketing campaigns and customer engagement efforts. Some standard features include the following:
- Campaign management: Marketing clouds provide tools for creating, managing, and executing marketing campaigns across various channels, such as email, social media, and mobile.
- Audience segmentation: Marketing clouds allow businesses to segment their audiences based on various criteria, such as demographics, behaviour, and past interactions with the brand, to deliver more targeted and personalised marketing messages.
- Personalization: Marketing clouds provide capabilities for creating personalised marketing messages and experiences for customers based on their preferences, behaviours, and past interactions with the brand.
- Analytics and reporting: Marketing clouds offer tools for tracking and measuring the performance of marketing campaigns across various channels, such as email open rates and social media engagement, to help businesses make data-driven decisions.
- Automation: Marketing clouds provide automation capabilities to help businesses streamline their marketing processes and reduce manual efforts, such as automated email campaigns or social media posts.
- Integration with other systems: Marketing clouds can integrate with other systems and technologies, such as customer relationship management (CRM) platforms or e-commerce systems, to provide a more holistic view of the customer journey.
- Mobile optimization: Marketing clouds provide tools for creating and optimising marketing campaigns for mobile devices, such as responsive email templates and mobile-friendly landing pages.
Example:
A multinational consumer goods company, Unilever uses Salesforce Marketing Cloud to manage its marketing campaigns across various channels, including email, social media, and mobile.

With Marketing Cloud, Unilever can segment its audience and deliver personalised marketing messages based on customer preferences and behaviours. The platform also provides analytics and reporting capabilities to help Unilever track and measure the performance of its campaigns, as well as automation features to streamline its marketing processes. Overall, Marketing Cloud helps Unilever deliver more effective and personalised customer marketing experiences while improving its marketing ROI.
FAQs
What is a marketing cloud?
Marketing Cloud is a suite of software tools that enables businesses to manage and optimise their marketing campaigns and customer engagement efforts across multiple channels, such as email, social media, and mobile.
What are some standard features of the marketing cloud?
Some common marketing cloud features include campaign management, audience segmentation, personalization, analytics and reporting, automation, integration with other systems, and mobile optimization.
What are the benefits of using the marketing cloud?
Marketing cloud can help businesses improve their marketing ROI by delivering more targeted and personalised marketing messages, streamlining marketing processes, and providing insights into campaign performance.
What are some examples of marketing cloud platforms?
Some examples of marketing cloud platforms include Salesforce Marketing Cloud, Adobe Marketing Cloud, Oracle Marketing Cloud, and IBM Marketing Cloud.
How do businesses use the marketing cloud?
Businesses can use the marketing cloud to create and execute campaigns across various channels, segment their audience, deliver personalised messaging, track and measure campaign performance, and automate marketing processes.
What is the future of the marketing cloud?
The future of the marketing cloud is likely to involve greater integration with AI and machine learning, more emphasis on data privacy and security, increasingly sophisticated personalization capabilities, expansion of marketing channels, and more seamless integration with other systems and technologies.
Marketing Channel
Definition
Marketing channels are a path through which products or services are moved from the manufacturer or provider to the end customer.
Description
A marketing or distribution channel is a set of intermediaries or middlemen involved in delivering a product or service from the manufacturer or provider to the end customer.
Marketing channels can be direct or indirect and involve different intermediaries, such as wholesalers, retailers, agents, or brokers. The choice of marketing channel depends on various factors, such as the nature of the product or service, the target market, and the company’s marketing objectives.

Source: www.freepik.com
The main functions of marketing channels are to facilitate the exchange of goods and services, reduce the cost of distribution, and provide value-added services such as financing, storage, and transportation. Therefore, effective management of marketing channels is critical for achieving marketing success and satisfying customer needs.
Importance of Marketing Channel
- Improved reach: Marketing channels enable businesses to reach a wider audience and expand their customer base through intermediaries who have established relationships with customers in various markets.
- Greater efficiency: By using marketing channels, businesses can streamline their distribution processes and reduce costs associated with storing, shipping, and handling products.
- Enhanced customer experience: Marketing channels provide customers with access to various products and services and value-added services such as financing and customer support, improving their overall experience.
- Increased sales and revenue: Effective management of marketing channels can result in increased sales and revenue, as businesses can reach more customers and offer their products in a broader range of markets.
- Competitive advantage: A well-managed marketing channel can provide a competitive advantage by enabling businesses to differentiate themselves from their competitors and offer unique value to their customers.
Powerful Marketing Channels
These are the powerful marketing channels:
- Social media marketing: Social media platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter offer businesses the ability to reach large audiences through targeted advertising and engaging content.
- Email marketing: Email marketing is a highly effective way to reach customers and promote products or services through personalised messaging and offers.
- Influencer marketing: Influencer marketing involves partnering with individuals who have a large following on social media or other platforms to promote products or services to their audience.
- Content marketing: Content marketing involves creating and sharing valuable, informative, and engaging content that attracts and retains a target audience.
- Search engine optimization (SEO): SEO involves optimising a website or online content to improve its ranking in search engine results pages and drive more traffic to a business’s website.
- Pay-per-click (PPC) advertising: PPC advertising involves paying for ad space on search engines, social media platforms, or other websites to drive traffic to a business’s website and increase sales.
- Affiliate marketing: Affiliate marketing involves partnering with other businesses or individuals to promote products or services and earn a commission on sales generated through their promotion.
How To Choose a Marketing Channel In 2023?
Choosing the right marketing channel in 2023 requires a strategic approach and consideration of several factors. Here are some steps to follow:
- Understand your target audience: Identify your target audience and their preferred communication and buying channels. Consider their demographics, behaviour, and preferences.
- Define your marketing goals: Determine your marketing objectives, such as increasing brand awareness, generating leads, or boosting sales, and align them with specific metrics to measure success.
- Evaluate your budget: Determine your available budget and the cost of implementing different marketing channels. Consider the ROI of each track and prioritise those that offer the highest potential return.
- Research your competition: Analyse and identify the marketing channels they are using successfully. Consider how you can differentiate yourself and offer unique value to your target audience.
- Test and measure: Experiment with different marketing channels and tactics and track their effectiveness using traffic, conversions, and revenue metrics. Adjust your approach based on the results and refine your strategy over time.
- Stay up-to-date: Keep abreast of industry trends and changes in consumer behaviour, and adapt your marketing strategy accordingly to stay relevant and practical.
Functions of Marketing Channels
Here are some functions of marketing channels presented in bullets:
- Facilitating the exchange process between producers and consumers.
- Providing a platform for products and services to be made available to customers.
- Creating efficiencies in the distribution process, reducing costs and increasing profitability.
- Offering value-added services such as financing, customer support, and after-sales service.
- Allowing for broader reach and greater market penetration by using intermediaries with established customer relationships in various markets.
- Providing market information to producers about consumer preferences, behaviour, and market trends.
- Allowing for differentiation and positioning of products through branding and marketing strategies.
- Providing a competitive advantage by enabling businesses to differentiate themselves from their competitors and offer unique value to their customers.
- Enabling businesses to establish and maintain customer relationships through direct and indirect communication channels.
Example:
Nike uses different marketing channels to reach and engage with its customers:

Source: www.google.com
- Retail stores: Nike operates worldwide, where customers can purchase its products and experience the brand firsthand.
- E-commerce: Nike also sells its products through its website, offering customers a convenient and direct way to purchase them.
- Social media: Nike uses social media platforms such as Instagram, Twitter, and Facebook to connect with customers, share its brand values, and promote its products through influencer partnerships and other marketing campaigns.
- Sponsorships: Nike sponsors various sports teams, athletes, and events, aligning its brand with high performance and athleticism.
- Advertising: Nike uses various forms of advertising, such as television commercials, billboards, and print ads, to promote its products and brand.
- Email marketing: Nike also uses email marketing to reach customers directly, offering personalised promotions and recommendations based on their previous purchases and browsing behaviour.
FAQs
What is a marketing channel?
A marketing channel is a set of intermediaries that a product or service goes through before it reaches the end customer. This can include wholesalers, retailers, distributors, and other intermediaries facilitating the exchange process between producers and consumers.
What are the functions of marketing channels?
Marketing channels perform various functions, such as facilitating the exchange process, creating efficiencies in distribution, providing value-added services, offering wider reach and greater market penetration, providing market information, enabling differentiation and positioning, and establishing relationships with customers.
What are the types of marketing channels?
There are two main types of marketing channels: direct and indirect. Direct marketing channels involve no intermediaries and enable producers to sell products directly to consumers. Indirect marketing channels involve intermediaries, such as wholesalers and retailers, that help distribute products to consumers.
How do you choose the right marketing channel for your business?
Choosing the right marketing channel depends on various factors, such as your product or service, target audience, budget, and marketing goals. It’s essential to conduct market research and analyse your options to determine which marketing channels will be the most effective for your business.
How do you measure the effectiveness of your marketing channels?
Measuring the effectiveness of your channels involves tracking metrics such as sales, customer acquisition costs, customer lifetime value, conversion rates, and return on investment (ROI). It’s important to regularly analyse and optimise your marketing channels to improve their effectiveness and drive sales.



