Customer Loyalty
Definition
Customer Loyalty defines an emotional bond between you and your customers. It indicates how willing a customer is to engage with your brand.
Description

In marketing, brands that are able to satisfy their customers and engage them with positive experiences become popular. Offering positive experience and overall value for services gives a boost to the business.
The latest statistics show that around 97% of customers get loyal to at least one brand. Three segments where customers show more loyalty than others include food 62%, personal electronics 44%, and fashion 57%.
It is also a proven fact that in common consumption, the consumable industry has a bigger loyalty rate compared to the fashion industry. A loyal customer is one who is not affected by availability or pricing until they get the same quality product. Businesses strive for loyal customers- ones who are interested to spend on a brand everytime they have a need for it.
Statista survey shows that 57% of customers are loyal to a brand based on customer service.
Whereas 54% of the customers became loyal based on the quality of the products offered. Retaining loyal customers with an increased retention rate of 5% pushes the profit by 25% to 95%.
Example:
Myntra makes their customers better engaged with them. The apparel and fashion brands motivate the buyers to shop and suggest their fashion style to others. In marketing, 92% of the customers are influenced by word-of-mouth recommendations.

The program by Myntra drives engagement by customers on its fashion and accessories platforms.
Ways to build customer loyalty
Building customer loyalty has its own advantage for brands. Some of them include:
- Reward loyal customers with loyalty programs: The most engaging way to build customer loyalty is by introducing loyalty programs. Introduce point system which helps customers earn points everytime after they make a purchase. These points get accumulated to offer discounts to the customers.
- Establish customer care for the brand: A customer looks up to your brand repeatedly only when you offer them good care. Establish customer care for all customers to develop loyalty in them.
- Email campaigns: Introduce email campaigns to motivate customers to make them more loyal. Encourage the customers to make repeat purchases by sending them emails for heavy discounts and offers.
- Create customer segmentation: Start with a loyalty program after customer segmentation. Divide the market based on age, gender, occupation, interests and engagements, etc. After segmentation, brands can design email campaigns based on customer’s interest.
- Add personalization: When you address your customers, try to make it personalised. Send personalised emails, push notification, and SMS on events to generate sales and motivate the customers to buy.
- Start with a business referral program: Create a program that help the customers earn reward or points when they refer the brand to their family or friends.
Importance of Customer-Loyalty program
Customer loyalty is important to increase profitability in business. This is how increasing customer loyalty will help you:
- Increase share-of-wallet: The customers who are loyal to your brand will contribute more to your earnings.
- Gives better word-of-mouth publicity: Loyal customers bring clients through word-of-mouth publicity. Loyal customers will tell their friends to buy ultimately leading to higher revenues.
- Better Trust: Customer loyalty strengthens a strong sense of trust between customers and brands.
Different types of Customer Loyalty Program
These are the types of customer loyalty program:
- Point based loyalty program: Under this loyalty program, regular customers accumulate points that can be exchanged for benefits like a promo coupon, a free gift, or some kind of exclusive offer. But this is where many businesses fall short: by complicating and confounding the connection between points and material incentives.
- Tiered loyalty program: As an initial incentive for joining the programme, offer modest prizes; as participants climb the loyalty ladder, stimulate repeat business by raising the value of the rewards. This prevents the possibility of members forgetting about their points (and never redeeming them) due to the too long interval between purchase and satisfaction.
- Value-based loyalty program: By providing value in ways unrelated to money, businesses can establish a special relationship with their target audience and encourage trust and loyalty.
- Partnership loyalty program: Strategic partnership is an effective way to retain customers. When you show your customers that you are offering something relevant, it shows them that you care.
FAQs
How can you measure customer loyalty?
These are the metrics that help you measure customer loyalty:
- Referral Traffic
- Social media mentions
- Customer Effort Score
- Purchase habits
- Customer retention rate
- Customer effort score
Why are customers loyal to the brand?
Customer loyalty is rooted to these factors:
- Expertise and services offered
- Authenticity
- Engagement
- Fun and Perks
- Trust
- Shared core values
- Personalised values
Why are customer loyalty programs effective?
Customer loyalty programs help you to engage more with your customers and build personalised relationships with your customers. It has a positive impact on profitability.
Customer Centricity
Definition
“Customer Centricity” is a company’s strategy that prioritises consumers’ demands and preferences at each stage of the customer journey.
Description
Understanding and anticipating customers’ needs and designing products, services, and experiences that meet those needs most effectively and efficiently possible.
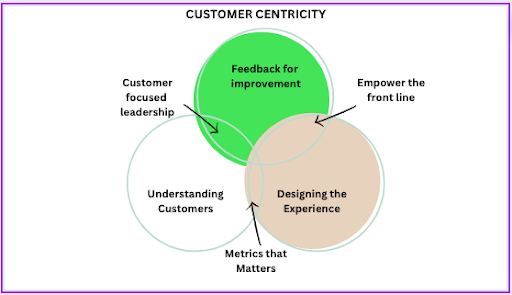
A customer-centric company focuses on building solid relationships with its customers, providing exceptional customer service, and creating a customer experience that is personalised, seamless, and enjoyable.
This approach requires a deep understanding of customer behaviour, preferences, and feedback and a commitment to continuous improvement and innovation.
In essence, customer-centricity is about putting the customer at the centre of everything a company does and using that focus to drive growth, loyalty, and long-term success.
Importance of Customer Centricity
Customer centricity is crucial for businesses that want to be successful in today’s competitive marketplace. Here are some of the key reasons why:
Increased customer satisfaction: By putting the customer at the centre of everything you do, you can create products, services, and experiences that truly meet their needs and desires. This can increase customer satisfaction and loyalty, driving repeat business and positive word-of-mouth referrals.
Competitive advantage: A customer-centric approach can help you differentiate your business from competitors. By offering a superior customer experience, you can stand out in a crowded marketplace and win more business.
Improved financial performance: Happy customers are more likely to spend more money with your business and refer others, leading to increased revenue and profitability.
Better customer insights: By focusing on the customer, you can gain valuable insights into their behaviour, preferences, and needs. This information can help you make more informed business decisions, develop better products and services, and effectively target your marketing efforts.
Continuous improvement: A customer-centric approach requires ongoing improvement and innovation. By constantly listening to customer feedback and making changes based on that feedback, you can stay ahead of the competition and continue to grow your business over time.
How to measure customer centricity?
Measuring the strength and the influence of customer centricity in an organisation is important as it helps to channelise the organisation’s activities towards the goal’s achievements.
Here are some key metrics and approaches that can help you assess the degree to which your business is customer-centric:
1. Customer satisfaction: One of the most important measures of customer centricity is customer satisfaction. Find out how satisfied the customers are through surveys, feedback forms, or other methods that allow you to gather feedback directly from your customers. A high level of customer satisfaction indicates that your business is excellently meeting your customers’ needs and desires.
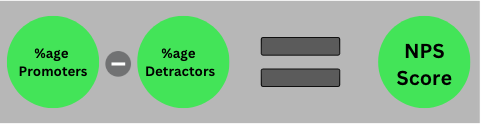
2. Net Promoter Score (NPS): NPS is a popular metric that measures the likelihood of a customer recommending your business to others. It is calculated by subtracting the percentage of detractors (customers who would not recommend your company) from the percentage of promoters (customers who would recommend your business). A high NPS indicates that your business is excellently satisfying your customers and creating loyal advocates.
3. Customer retention rate: Another important metric for measuring customer centricity is customer retention. This measures the percentage of customers who return to your business after their initial purchase. A high retention rate indicates that your business is excellently building long-term relationships with your customers.
4. Customer lifetime value (CLV): CLV measures the total value a customer brings to your business over their relationship with you. A high CLV indicates that your business is booming at creating loyal customers who continue to make repeat purchases.

5. Employee engagement: Employee engagement is also an important factor in customer centricity. Engaged employees are more likely to provide exceptional customer service and create positive customer experiences. You can measure employee engagement through surveys, feedback forms, or other methods that allow you to gather feedback directly from your employees.
How to Create a Customer Centric Strategy For Your Business?
Creating a customer-centric strategy for your business involves several key steps:
- Understand your customers: The first step in creating a customer-centric strategy is to deeply understand your customers, their needs, desires, and pain points. Collect customer behaviour and preferences data, and use that information to inform your product and service offerings.
- Empower employees: Creating a customer-centric culture requires empowering employees to provide exceptional customer service. This means providing ongoing training and support and creating a work environment that fosters empathy and a deep understanding of customer needs.
- Personalised experiences: A vital component of a customer-centric strategy is personalization. Use data and technology to tailor experiences to individual customer needs and preferences, such as targeted marketing campaigns and personalised product recommendations.
- Optimise touchpoints: A truly customer-centric business must optimise the customer experience across all touchpoints, from the initial point of contact to the final purchase. This may involve improving the website or mobile app design, streamlining checkout and payment processes, and offering fast and reliable shipping and delivery options.
- Gather feedback: Finally, a customer-centric strategy requires ongoing feedback and iteration. Gather feedback from customers and employees regularly, and use that feedback to inform business decisions and improve the customer experience.
Anatomy of Customer Centricity
The anatomy of customer centricity involves several key components, including:
- Customer focus: At the core of customer centricity is a deep focus on understanding and meeting customers’ needs. This involves collecting and analysing data on customer behaviour, preferences, and feedback and using that information to design products, services, and experiences that truly meet their needs.
- Culture of empathy: A customer-centric company values empathy for customers and employees. This means creating a supportive and empowering environment for employees and providing the tools and resources they need to deliver exceptional customer service.
- Personalization: A customer-centric business takes a personalised approach to interact with customers, using data and technology to tailor experiences to individual needs and preferences. This may involve targeted marketing campaigns, personalised product recommendations, and customised customer support.
- Seamless experiences: Customer-centric companies prioritise creating seamless experiences for their customers, from the initial point of contact to the final purchase. This may involve optimising the user experience on your website or mobile app, providing fast and reliable shipping and delivery options, and offering easy returns and exchanges.
- Continuous improvement: A customer-centric business is committed to constant improvement and innovation. This means listening closely to customer feedback, incorporating that feedback into business decisions, and proactively seeking ways to improve the customer experience and stay ahead of the competition.
Example
One brand that is often cited as an example of customer-centricity is Amazon. Amazon focuses on the customer, from its extensive product selection to its fast and reliable delivery options, which is evident in everything they do. They have built their business around the customer experience, with features like personalised recommendations, easy returns, and a simple and intuitive shopping interface.
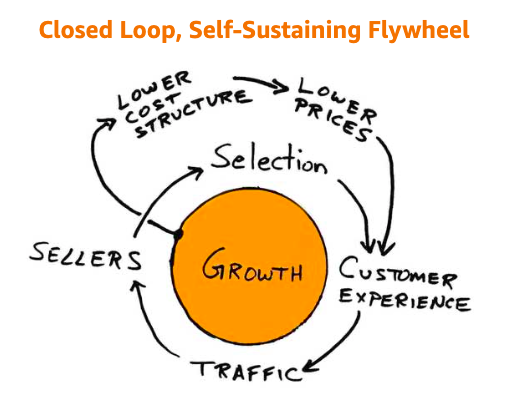
Amazon’s customer-centric approach has allowed them to become one of the most successful companies in the world, with a loyal and dedicated customer base.
They are constantly innovating and improving their services to better meet the needs of their customers, and they are known for listening closely to customer feedback and incorporating it into their business decisions.
Overall, Amazon’s commitment to putting the customer first has allowed them to build a brand synonymous with convenience, quality, and customer satisfaction.
FAQs:
Why is customer-centricity important?
Customer centricity is essential because it can increase customer satisfaction, loyalty, advocacy, improved financial performance, and competitive advantage.
By putting the customer at the centre of everything you do, you can create products, services, and experiences that truly meet their needs and desires.
How can I become more customer-centric?
Becoming more customer-centric involves several key steps, including collecting and analysing customer behaviour and preferences, empowering employees to provide exceptional customer service, creating personalised experiences for customers, optimising the customer experience across all touchpoints, and constantly seeking feedback and making improvements based on that feedback.
What are some common challenges to achieving customer centricity?
Some common challenges to achieving customer-centricity include limited access to customer data, lack of employee buy-in, outdated technology or processes, and difficulty measuring the impact of customer-centric initiatives.
These challenges may require new technology, cultural shifts, and ongoing education and training.
How can I measure the success of my customer-centric initiatives?
Measuring the success of your customer-centric initiatives requires a combination of quantitative and qualitative data, as well as a deep understanding of your customers and their needs.
Key metrics include customer satisfaction, Net Promoter Score (NPS), customer retention rate, customer lifetime value (CLV), and employee engagement.
In addition, gathering feedback directly from customers and employees can also be valuable in assessing the success of your customer-centric initiatives.
What are the three pillars of customer centricity?
These businesses rely on three key strategies: customer development, customer retention, and customer acquisition to establish and maintain a customer-centric business model.
Cookie
Definition
Cookies are text files that include small bits of information, such as a login and password, and are used to recognise your machine when you’re connected to a computer network.
Description
It gets convenient to browse for information when the system remembers the user’s preference. This is where a cookie can help. Cookies are typically used to remember user preferences, login credentials, and other information related to a user’s interaction with the website or application.

Cookies can also track user behaviour and gather data for analytics and advertising purposes. Cookies are commonly used in web development and are supported by most modern web browsers.
Importance of Cookies
Cookies are important for several reasons:
Personalization: Cookies can be used to remember a user’s preferences and settings, such as language preference, font size, and colour scheme. This can improve the user experience by making the website more personalised and tailored to users’ needs.
User Authentication: Cookies are often used to authenticate and keep users logged in. This means that users do not need to log in every time they visit a website, which can save time and improve the user experience.
Session Management: It can be used to track a user’s session on a website, which helps maintain the state between pages and ensure that user data is consistent.
Session Management: Cookies can be used to track a user’s session on a website, which helps maintain the state between pages and ensure that user data is consistent.
Analytics and Advertising: It can be used to track user behaviour on a website and gather data for analytics and advertising purposes. This can help website owners to better understand their audience and optimise their websites for better performance.
How does cookies work?
This is how a cookie work:
- The user visits a website for the first time: When a user visits a website for the first time, the website sends a small data file to the user’s browser, which is stored on the user’s device. This data file is called a cookie.
- The browser stores the cookie: The browser keeps the cookie on the user’s device, typically in a designated folder or cache.
- The user returns to the website: When the user returns to the website, the browser sends the cookie back to the website.
- The website reads the cookie: The website can then read the information in the cookie, such as user preferences, login credentials, or other data.
- The website uses the information: The website can use the information in the cookie to personalise the user’s experience, keep the user logged in, or perform other functions.
- The cookie can be updated or deleted: The website can edit or delete the information in the cookie as needed and set an expiration date to ensure that it is not stored indefinitely.
- Users can manage cookies: Users can block or delete cookies anytime through their browser settings.
What is the future of cookies in marketing?
Here are some key points about the future of cookies in marketing:
- Changes in browser and privacy regulations make it more difficult for advertisers to track user behaviour and deliver targeted advertising using cookies.
- First-party data and alternative technologies, such as machine learning and artificial intelligence, can personalise user experiences and deliver targeted advertising without relying on cookies.
- Marketers must adapt to new technologies and strategies to continue delivering personalised and effective marketing campaigns.
How to capture data without cookies?
There are several ways to capture data without relying on traditional cookies:
- Device fingerprinting: Device fingerprinting involves collecting information about a user’s device, such as the device’s operating system, browser version, and screen resolution. This information can be used to create a unique identifier for the device, which can be used to track the user’s behaviour and deliver personalised content and advertising.
- IP tracking: IP tracking involves collecting the IP address of a user’s device, which can be used to determine their approximate location and track their behaviour. This information can be used to deliver personalised content and advertising.
- Login and registration data: Marketers can collect data from users when they log in or register for a website or app. This data can include personal information such as the user’s name, email address, and preferences. This information can be used to deliver personalised content and advertising.
- Analytics tools: Marketers can use analytics tools such as Google Analytics to collect data about user behaviour on a website or app. This data can include page views, session length, and user demographics. This information can improve the user experience and deliver targeted advertising.
- Surveys and feedback: Marketers can collect user data through surveys and feedback forms. This data can include information about user preferences, interests, and behaviours. This information can be used to deliver personalised content and advertising.
Benefits of Cookie
Cookies offer several benefits for both website owners and users. Here are some of the key benefits of cookies:
- Personalization: It allow website owners to personalise the user experience based on the user’s previous interactions with the website. For example, cookies can be used to remember a user’s login information, language preference, or shopping cart contents.
- Convenience: It makes it more convenient for users to navigate a website by remembering their preferences and settings. For example, cookies can remember a user’s preferred language or font size, so they don’t have to set it every time they visit the website.
- Analytics: It can be used to collect data about user behaviour on a website, such as pageviews, session length, and user demographics. This data can be used to improve the user experience and make data-driven decisions about website design and content.
- Advertising: It can be used to deliver targeted advertising to users based on their browsing history and behaviour. This can help advertisers reach their target audience more effectively and improve the return on investment for their advertising campaigns.
FAQ
What is a cookie?
A cookie is a small text file stored on a user’s computer or mobile device when they visit a website.
What is the purpose of a cookie?
The purpose of a cookie is to remember user preferences and settings, provide personalised content and advertising, and collect data about user behaviour on a website.
Are cookies safe?
Yes, cookies are generally considered safe. They cannot access any information stored on a user’s computer or mobile device, and they do not contain any viruses or malware.
Can I block cookie?
Yes, most web browsers allow users to block or delete cookies. However, blocking cookies may affect certain websites’ functionality and user experience.
What is the difference between first-party and third-party cookies?
First-party cookies are set by the website the user is visiting, while third-party cookies are set by a domain other than the one the user is visiting.
Why are cookies important for online advertising?
Cookies are important for online advertising because they allow advertisers to track user behaviour and deliver targeted advertising based on that behaviour.
What are some alternatives to cookie for tracking user behaviour?
Alternatives to cookies for tracking user behaviour include device fingerprinting, IP tracking, login and registration data, analytics tools, and surveys and feedback.
What is the future of cookie in marketing?
The future of cookie in marketing is still being determined due to changes in browser and privacy regulations. Marketers will need to adapt to new technologies and strategies to deliver personalised and effective marketing campaigns.
Barter
Definition
Barter is trading goods and services between two parties without using a monetary system. The two parties involved can be individuals, advertisers, and businesses.
Description
Corporate barter is a valuable marketing strategy to solve financial problems. It helped businesses manage liquidation of excess and obsolete inventory. This enabled businesses to enter new markets without incurring any new investment cost.
The Mesopotamian tribe started bartering in 6000 BC. It was a convenient method of getting food, spices, weapons or anything in exchange for goods. Gradually, through the 18th century, retailers completely ignored the barter trading system.

It still exists in the markets that include business-to-business space and consumer service. This online barter system became popular with small businesses, especially after 2008, when small businesses were finding ways to survive. This system saved the businesses and led to an increase in sales and revenue generation.
Much later, increased competition and pandemic affected small and medium businesses more than it did to the large scale business. They looked for barter to save money yet grow their business.
Barter in marketing related to corporate trade companies that worked with a media buying agency to find the perfect place for media placement. They offered trade credits when products and services were bartered.
Gradually, with this system in modern economies companies can trade for advertising rights. under which they can sell ad space to another company.
How can bartering help increase cash flow?
Barter in today’s time can happen on online platforms amongst individuals as well as with Fortune 500 companies. But because economies are under shock due to the war and the pandemic, bartering is confirmed to make a comeback.
For some other reasons, bartering can be accepted widely due to the sudden dip in the financial market situations and the rise in the price of commodities at the global level.
And there is nothing unacceptable about the situation because that is the way economies will be able to survive and make a comeback.
Things to Keep in Mind for Barter
Barter has been rooted in and around the market for ages. And to make it a flawless system, here are a few things you must note if you are entering into this system:
- Be Transparent: Both parties need to be transparent and inform each other of what they are looking for in their service or product.
- Know your worth: You should be capable of knowing the worth of the service you want to barter against. It will help you choose exactly what product will help.
- Approach a potential barter: Approaching a possible barter which has creativity and flexibility to understand the counteroffer.
- Think about a long-term relationship: You must barter with an individual or a company with which you can stay connected for a long business relationship.
Benefits of bartering in marketing
Bartering is practised in local and international markets to sustain businesses in competitive markets.
The Internet has made several companies efficient in the industry even when the conditions are not favourable. Barter can increase the efficiency of the business’s houses, reduce management costs, and match the demand. These are the benefits of bartering in today’s time:
- Flexibility: Bartering gives businesses the flexibility to exchange related products. Like it offers an opportunity to trade advertising spaces.
- Cash Savings: Businesses can get needed products or services without spending money. It allows companies to keep cash in reserve, which is essential for small businesses.
- Makes business simple: Barter makes complex businesses simple and helps when companies or individuals are low on cash. A watch-making brand and an artificial jewellery-making company can offer each other’s products in their commercial spaces. So rather than money, they give businesses space to sell their products. In addition, it provides each of the brands an opportunity for publicity.
Example
National Textile Corporation (a PSU in India) leveraged media barter in lieu of yarn and grey raw material. They saved about 15-20% on media spending.
FAQs
Is bartering possible with consumer service?
Yes, bartering is possible with consumer service.
What are some examples of bartering for consumer service?
Some common examples of bartering for consumer service are tax preparations, financial planning, computer repair, medical care, and lodging.
What are the platforms for modern advertising services?
Modern advertising bartering can be available on the Internet, billboards, radio rights, and television.
What is barter marketing?
Barter marketing works with media buying agencies to find apt media placements and fund the ad order without cash.
What are barter agencies?
Barter agencies buy media from sellers willing to sell it in exchange for some services. These agencies buy media from suppliers who are lesser-known publishers who are looking to increase their revenue. The barter agency sells media that it has already purchased.
Also Read –
Behavioural Targeting
Definition
Behavioural targeting is a marketing method to use consumer activities to strengthen their advertising campaigns.
Description
In the competitive market, brands are required to reach their audience with highly personalised messaging. But to increase the engagement, it is important for brands to know how their audience interacts with the brand.
To observe interaction, digital or online marketing activities are all backed by AI and ML tools. These tools make marketing convenient for the brands as they understand what the users are actually looking for.
Behavioural targeting is noting people’s actions to find out which message or advertisements will resonate with them. The information about the user’s behaviour is stored as data.
In the days of traditional marketing, a lot of resources like money and efforts were wasted because marketers did not know whom to target and how much. But now the marketers are aware and they approach their audience by observing their behavioural data.
In today’s time, random marketing can be challenging for brands. The competition is high which is why adapting to new techniques of customer’s data management from studying behaviour can offer a higher conversion rate.
Behavioural targeting makes highly personalised marketing possible for the right time by using real-time information about actions about what visitors are doing on the website or application.
The main intent of using this technique is to deliver marketing messages to those who are interested in it. The data is based on purchase history, frequently visited websites, web searches, etc.
Behavioural data is about what people are doing on your website or with your campaigns.
Types of Behavioural Targeting
These are the types of behavioural targeting:
- Website Engagement: You can target your audience when they are on your website by surfacing them with pop-ups, promotional ads, and links to other related content which interests them. It enhances the user-experience and engages the visitors for a time longer than usual.
- Purchase Behaviour: Use purchase behaviour to target the audience and suggest them with similar products they would like to shop. It is a perfect example of recommending products based on the purchase behaviour. Knowing what lies in the cart of the customers can help to target the audience.
- Campaign Engagement: Campaign engagement is sending emails to your target audience. You can know who opens your email and who doesn’t. This can help you organise the audience and you can resend the emails to non-openers and to people who engaged with the campaign email.
- App Engagement: By observing the engagement of the individuals with the app, you can find out who is opening the app. You can then send personalised messages to the users. Like if the user has not opened the app, they can open it and the ones who have completed a stage can be congratulated for completing it.
Importance of behavioural targeting
Behavioural Targeting is important to engage the audience with the brand for a longer time. To engage the user of your website or app, personalised messaging is important.
↑ Message Personalisation = ↑ High Response
Personalised messages sent to the target audience at the right moment increases the likelihood that the audience engages more with the content.
Behavioural targeting is important for both consumers as well as businesses because:
- Allows to send relevant content to the audience: Behavioural targeting makes it easier and faster for the audience to conduct online research and make purchase decisions.
- Accurate decision making: Behavioural marketing allows the brand to make informed decisions because they know what exactly and when is the audience interacting with the brand.
- Create contact profiles: Behavioural targeting allows companies to create customers profiles and organise them into different segments. It helps companies to serve the content that interests the customers.
- Higher ROI: Personalised marketing encourages the customers to engage for a longer time. It increases the chances of higher ROI with the higher click-through and conversion rates.
How behavioural targeting works?
Process of behavioural targeting includes collecting data, sorting it and delivering customised messages to individual users. The three step process is explained below:
- Data Collection
Data about customer’s behaviour is collected from different sources like mobile apps, mobile device data, third-party data parties, websites, CRMs, marketing survey companies, etc.
For example, a few websites use cookies to track data about the consumer behaviour, places at which they click the most. This data collected is stored in data management platforms to automate marketing systems.
- Segmentation
Data segmentation is the second step where users are segmented based on their behaviour. Like people using Apple ipods and those using Android products can be segmented into different groups.
- Targeting
The third step is targeting. In this step, advertisers choose a specific group. The aim of targeting the group is to have the most relevant users. The targeting is based on matching the interest and behaviour of the visitors. Targeting helps businesses with high conversion rates.
Example
Neutrogena, a beauty brand, uses customer’s past shopping behaviour to push their sales ahead. 75% of the customers they had were making purchases from one segment of the products. The brand then used the past buying history and created product pairing. It increased the sales for them as the sales were made on behavioural targeting.
FAQs
How does behavioural targeting work in marketing?
Behavioural targeting is the game of expanding business on the basis of the customer’s behavioural data like their buying history. This is how behavioural targeting works:
- Cookies: Cookies are placed on the website of the users who visit the new website. These cookies are stored temporarily or permanently. It helps the website owner collect quite some sufficient data about the users.
- User profile: After the user stays on the webpage, clicks ads and spends time, their behavioural data is collected.
- Target market groups: After the user’s profile is created, companies can separate the users into different groups. The groups are made depending on the likes and dislikes, trends and interests. The company can then use the data for the target marketing.
- Custom content is shared: When the groups are made, the users will only receive custom content and personalised ad materials. The information displayed will depend on past behaviours.
What are the advantages of behavioural targeting for advertisers?
These are the advantages of behavioural targeting for advertisers:
- Better user engagement in terms that with behavioural targeting, more meaningful information is shared with the users.
- More click-through rates as users spend more time on the website which increases the probability of ad clicks
- Higher revenue comes from more ad clicks.
- Better customer insights.
- Improved conversions.
What are the benefits to the users when you talk of behavioural targeting?
These are the advantages the users will have from behavioural targeting:
- Better user experience as they will see the content of their interests.
- Higher efficiency because the ads and the recommendations on the website keep reminding the user about their past searches.
- Receive product alerts through ads to keep the customers informed.
Biddable Media
Definition
Biddable media is the process of buying advertising space through real-time bidding. Advertisers bid to get maximum impressions or leads.
Description
Suppose you own a shop which is in a new mall that is in the centre of the city. You sell electronic items there. The place was high in demand and for the shop you had to go for a lottery system. When your name was chosen in the lottery, you got the opportunity to sell your products.
Similarly, for ad space on the website or blogs, you have biddable media that helps advertisers to bid and buy the ad space.
The interest in a particular ad space is high because of the high probability that the number of visitors will be more.
More the number of customers, higher will be the traffic which will generate conversions and improve sales.
Facebook shows a 38% YoY growth in terms of increasing investment in terms of advertising revenue into these social media channels. Other than Facebook, Google’s advertising revenue rose by 69% whilst that of YouTube grew by 84%.
For auction, the top spot on a popular Google Search Engine Results Page (SERP) is costly.
This is why a little bit of research like monitoring the ad performance before bidding is helpful. If at a particular place, an ad is performing well, it is important that you as an advertiser offer a high bid for it.
Example
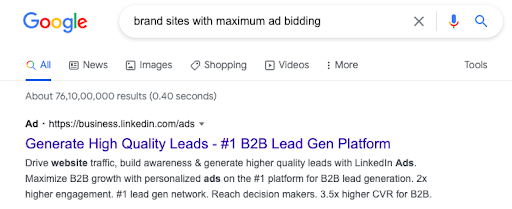
Above is an example of how the website google.com provides advertisers an opportunity to display their ads. It is the most fancied and high-in-demand place where advertisers look to place their products. Though Google has its own criteria to select the display ads still the bidding process is up for it.
FAQs
What are the prominent biddable media channels that advertisers can consider?
These are the biddable media channels that advertisers can consider:
Pay-Per-Click: The display ads that are shown in the Google SERP amongst the top results are PPC ads. Businesses bid for this position to get the attention of the users.
Social media platforms: Amongst the few biddable platforms, Facebook offers to target the audience based on their interest, activities, and behaviour. It also allows bidding after segmenting the audience based on location, age, and gender.
YouTube: YouTube is the most popular video sharing platform that allows users to bid for ads. YouTube works on ads per view. The prices for bidding is higher when the ads are placed on the most popular search terms.
What do you think are the benefits of biddable media?
These are the benefits of biddable media:
- Helps drive increased traffic to your website.
- With more traffic, the sales increases.
- It helps you to connect with the target audience.
Brand Identity
Definition
Brand identity is how a brand portrays itself to the customers. A brand is not a logo but a logo represents a brand.
Description
Branding is the process of marketing for a brand that creates a perception about it in the minds of the customers.
The visible elements of a brand like the colour, design, and logo refers to brand identity. These are the elements that distinguish a brand from the competitors.
Before making profits, it is important to establish a strong brand identity that reminds people of you. It is a kind of promise that you make to your customers.
When you inspire your customers with your thoughts and what you express, they develop a sense of loyalty for your brand. This is why a brand’s identity is important.

Brand’s identity pushes people to spend money. If customers have a strong and memorable experience with the brand, they are most likely to stick to it for a long time.
Importance of Brand Identity
Brand identity is what makes a brand memorable and uniquely identifiable. This is why a brand identity is important:
1. Helps build a suitable brand image
Brand image gives rise to the identity of a business and that is important. A brand image reminds people about it, keeping them engaged.
2. Differentiates the product from the competition
A brand identity gives brands a unique stance and help them differentiate themselves from the market. It gets a loyal customer base for the brands.
3. Create consistency
Brand identity places a consistent idea about the brands to help people connect with it in the same way always.
4. Defines a personality of the brand
Brand identity makes it easier for the brand to express their brand personality. It aids in engaging people for longer with the brand.
How to Create a Brand Identity?
Building a brand is not a job to be done in a day’s time. It takes days and months to do so. Some important steps to establish a brand identity include:
Step 1: Researching audience, value proposition, and competition
The first step in creating a brand is to conduct market research. Find out the pain points of your target audience because you cannot hit the market for all.
There has to be a segment to which you may cater to different needs. Specify an audience because you cannot market your product to men if it is for women.
Identify why your business is unique and how you can stand out from the competition. Conduct a SWOT analysis and establish how best you can capture the market.
Step 2: Design the logo
Logo is a vital element when you want to decide the brand identity. It goes everywhere on the website, cards, apparels, and online ads.
Logo helps people connect with your brand hence it is important you make it visually appealing using brand colours. Keep the brand consistent across documents but leave room for flexibility of tags and lines you use for advertising.
Step 3: Decide the language you want to use on social media to connect and advertise.
Use language that matches the personality of your brand. Establish an emotional connection with the consumers to get heard by your target audience.
Step 4: Know what to avoid
A brand should not confuse the target audience and avoid copying the competitors.Keep the brand message consistent both online and offline.
Step 5: Monitor your brand
Use analytic tools like Google Analytics to monitor brand’s performance online. You can also use surveys and social media discussions,etc to track key performance metrics.
Example

Hearing the name Coca-Cola reminds you of the red colour that the brand carries. It elicits confidence that people carry when they consume the drink.
The brand has always portrayed that one must enjoy coke with family, friends, and encourage sharing happiness over Coca-Cola.
FAQs
What are the factors that affect the brand identity?
For a brand, these are the factors that affect the brand identity:
- Market size affects branding strategy ultimately affecting the brand identity.
- Competition affects branding as then you have to inform the customers why you are different from the competitors.
- Scarce company resources affect the brand identity. To save on time and investment on resources, all products are kept under one brand.
- New product introductions can affect the brand identity as with the new products old one’s lose attention.
- Innovation and technology that leads to development affects the brand. Businesses need to stay updated on how they bring the brand in front of the audiences.
How does creating a brand identity help brands and the target audience ?
Creating a brand identity helps brand in the following ways:
Defines personality: A brand identity helps to communicate their thoughts and values to connect with their audience. These thoughts can evoke feelings in the audience who will buy the product. The brand logo of Airbnb looks like the letter ‘A’ which also indicates a heart when reversed upside down. The logo indicated “people”, “place”, “love” and “letter A”.
Consistency: A brand identity is important to be consistent which implies that it should give the same message in all marketing activities. The consistent message that the brand has given to its customers is that they can be as comfortable as they are at home and not just any house.
Differentiate: A brand identity helps the brand stand distinctly from another brand. Coca Cola stood different from Pepsi in the emotion that the former exhibited strength whereas Pepsi stands for smartness, fun, and youthfulness. In another story, Airbnb differentiated itself in the sense that they allowed people to experience the world in rental accommodations which are hosted by locals.
Awareness: The target audience should know that a brand exists and how it looks. It helps people connect more conveniently with the brand. Airbnb has made its customers aware to a point where they use the brand as a verb. It is like Airbnb-renting a house.
Loyalty: A brand identity develops a feeling of loyalty in customers. Like Airbnb, brand identity speaks of “Belong Anywhere”. The idea is to give comfort to the users and inform them that they will be taken care of during their stays.
What are the types of brands?
These are the types of brand one can define:
- Corporate branding: It is a method that businesses use to sell themselves in order to stand out from the competitors. To do this, they decide on a number of crucial factors, including pricing, mission, target market, and values.
- Personal Brands: Social media and other platforms are used by people to create their own personalities and strengthen their brands. Regular social media updates, the sharing of photos and videos, and setting up meet-and-greets all fall under this category.
- Product Brands: Also referred to as merchandise branding, this sort of branding focuses on marketing a single item. Conducting market research and selecting the ideal target market are necessary for branding a product.
- Service Brands: This type of branding is used for services, which frequently calls for some innovation and creativity because you can’t physically display services.
Brand Strategy
Definition
A long term plan that focuses on the development of the brand is referred to as brand strategy.
Description
A brand becomes successful when it serves its clients well and offers them what the brand promises. Taking the brand longer in its journey with all length and breadth is all dependent on the brand’s strategy.
When a brand has a strong and influential strategy, the customers associate well with it. And when customers associate strongly with the brand, it helps drive the purchase decision.
For a successful brand strategy, things must fall into place from planning to execution. A brand should start with setting up their goals right. They should identify their target audience that strengthens the purpose of the brand.
Importance of Brand Strategy
These are the reasons why brand strategy is important:
- A brand strategy communicates your core value: A brand strategy helps you lay the foundation on how to attract loyal customers. It makes it easy to communicate your brand message to your customers.
- Brand strategy helps to identify weaknesses: Defining a brand strategy enables a company to offer consistent experience to their customers. When a brand meets expectations of the customers, it gains popularity.
- Increases accountability: Strategy building helps you stay on track. Every stage of development can be followed to keep productivity in line.
- Saves money and efforts: With strategy building you can hit the maximum return on investment. You can quickly put A/B testing to keep business strategy aligned with the goals.
- Increases the valuation of the company: Brand strategy helps you increase the valuation of the company. With a clearly defined strategy you can approach the investors and ask for funding to push the growth in the business.
- Aligns all departments: A strategy pulls every department to remain aligned with the organisational goals. It gives an opportunity for a quick process check where the deliverables are not met.
Future trends of Brand Strategy
Branding is neither a one time activity nor does it bring results overnight. After the pandemic and the global recession, brands will have to reconsider their brands. They will have to rethink their mission, vision,and strategies.
Change in the perspective of how the target audience perceives the brand and what they are expecting in the future will affect the branding strategy for the companies. To make a lasting impression and keep the target audience engaged , this is what the brands can do in future:
1. Make it nostalgic yet modern
The first trend for branding strategy that brands can follow is to pull the heartstrings of their customers and approach them to keep them engaged and vibrant. The trick will help to ensure that the brand remains timelessly active over the years.
2. Use powerful colours
Brands can use impactful colour combinations that yet suit the tone of the brand. Because digital platforms are the major spaces that can catch the attention of the visitors, use of vibrant colours can help companies touch the mind and memory of their customers. Using brand colours with a touch of vibrance will boost brand recognition.
3. Break the boundaries
Breaking boundaries will be the crucial trend when the competition amongst each brand is to rise. Companies can refer to the archaic and traditional styles of branding and choose broken design rules with bold colours.
4. Eco-branding
Brands can choose eco-branding to move in a minimal futuristic direction. Brands can prefer earthy tones as well to impress in a unique way.
5. Animated Logos
Animation will still rule the branding purposes. It is a distinct way to connect with the audience in an intriguing and entertaining way. The current moving logo of Google is a perfect example to represent search engine’s services in speed and style.
6. Impressive Typography
A brand can choose statement typography to spread the message in an impressive way. Try to keep the font consistent across all touchpoints for branding purposes.
How to make a brand strategy?
Making a winning brand strategy is important for a business to flourish.
Step 1: Find your core beliefs
Establishing your core beliefs is the first stage in developing your brand strategy. Your brand’s core values are the ideas that guide your behaviour. These essential principles connect to the specific issues you want to resolve for your consumers and are the reason why your business exists.
These principles were frequently created at the company’s foundation, and they are unlikely to change significantly as your business expands. They serve as the main tenet of your brand strategy.
Step 2: Create a positioning statement
Your product and your target market are both described in your positioning statement.
Its goal is to demonstrate precisely how your product meets a specific need in a target market. Make use of a positioning statement as a tool to ensure that your marketing initiatives and brand strategy are complementary. To develop brand positioning statement, you have to find clarity on these:
- Who do you serve?
- What do you offer them?
- How do you offer your target audience?
- How are you different from the current offers?
Step 3: Understand your customer profile
A description of the kind of consumer who would benefit greatly from your product or service is called an ideal customer profile.
They are the most straightforward to offer, have the highest retention rates, and adore recommending your goods to others. The ideal customer profile, in essence, is a description of potential clients who have the traits of your most significant successes.
Step 4: Prepare a brand promise
A tagline’s succinctness and your USP are combined to create a powerful brand promise. Any brand’s brand strategy gets more successful the more they live up to their promises. In contrast, if you fall short of your customers’ expectations, your brand strategy is failing.
It is crucial to develop a worthwhile brand promise that is both thrilling and realistic given the danger of not living up to it.
Step 5: Have a visual identity
Your brand’s overall description of its pictures and other outward manifestations is known as its visual identity. Everything related to your website, business cards, and social media profiles is part of your visual brand.
Step 6: Review customer touchpoints
Keep the brand strategy consistent across all brand touchpoints. It is a contact between you and your brand.
Step 7: Define brand voice
The key to a successful brand strategy is to define your brand’s voice. A brand voice defines how you always speak to your audience. The brand voice should connect with your ideal client. Easiest is to stay true to the brand to define the brand voice.
These two components work together to create an authentic look. The voice adopts a more authoritative tone for some businesses. Others find that a voice that is more jovial sounds more genuine.
Step 8: Brand audit
Check how brand strategy performs in comparison to other goals. Evaluate how well you have been able to represent your core values to connect with the audience. Audits help you to establish performance benchmarks enabling you to consistently improve brand strategy.
Example
Apple’s branding strategy started with the “Think Different” Campaign. They had to think uniquely to convince people to buy their products to exhibit what they believe.
Apple’s products look and work differently. It gave a message of creativity that people can try with Apple’s products.
FAQs
What are the components of Brand Strategy?
These are the components of Brand Strategy:
1. Purpose: A brand has to establish the purpose of their existence and that of their products. They should know how their products will help the customers and then they can make a strategy.
2. Consistency: Consistency involves aspects of the same colour, same fonts and style of language. It makes it easier for customers to recognise the brand.
3. Emotion: Learn what emotion a brand feels to evoke in the customers. Company needs to foster an emotion to connect with the target audience.
4. Employees involvement: A company cannot sail in the market without the efforts of its team and employees. The employees must carry the same ideas as that of the brand. The team should be trained so that they resonate the same thoughts about a brand.
What are the five elements of a good brand strategy?
These are the five elements of a good brand strategy:
- Brand design
- Brand voice
- Brand values
- Brand vibe
- Brand story
What happens without a brand strategy?
Without a brand strategy, a company can fail because :
- They do not have a mission, values, or purpose.
- They lack a marketing plan without which moving will be non-directional.
- There will be no team alignment and the outputs will be derailed.
- The brand will takes ages to carve a niche for itself.
Cost Per Click (CPC)
Definition
Cost per Click refers to the cost you incur on each click on the ad. It refers to the highest amount you are willing to pay when someone’s click on an ad.
Description

For online business, you run different advertisements. And for a successful revenue generation, it is relevant that you run advertisements. The cost per click, determines the financial success of your paid ad campaign.

CPC determines how much Google Ads will cost for you in an online advertising revenue model. Website owners or publishers bill advertisers for displaying their ads on their platform. They quantify the cost based on the number of times visitors click on the ad.
After you run ads, Google algorithms evaluate the ads and does not charge you more than the bids. Google provides discounts to those who have high ad quality scores.
Example
Arun, an apparel business owner, wanted to grow his business online. He started with his e-commerce website and promoted it via other platforms. Arun started with an ad-campaign for which he paid Rs. 11,000/-.
The campaign had received around 150 clicks. This signifies that the cost per click will be CPC= 11000/150 = Rs 73.33/-
Ways to reduce Cost per Click
Rise in competition has resulted in ever increasing cost of advertisements. This means that you need to strategize your campaigns preventing excess money flow out of the pocket. You can reduce the cost per click by:
- Raising the Quality Score: Quality score defines the quality of your ad in comparison to that of others.
- Expected Clickthrough Rate: Edit the ads so that a larger part of your target audience gets fascinated and click on the ads.
- Ad Relevance: Make sure that the ad is relevant for the target audience. It should match their search intent.
- Landing page experience: The load time of the landing page should be high especially on mobile devices so that the customers are engaged for a longer time.
- Keyword Research: Keyword research helps you drive your advertisements and match it to the searcher’s intent. A few techniques that can take you close to keyword research include Target>> Split>>Group
- Target: Target the audience with the keywords the audience are searching for and which matches their intent.
- Split: You can split the target keywords and make different ad groups to match the user’s search intent.
- Grouping: Create themes for different products and services. Then you can market the products with keywords accordingly.
How to calculate Cost Per Click?
Cost per Click is derived by dividing the cost of an advertising campaign by the number of clicks.
Cost per Click= Advertising Cost/ Number of Clicks
When you use any advertising software, you bid on keywords to display paid ads. Different types of aspect involved in cost per click are:
Average Cost per Click: It is the average an advertiser will spend for every ad click.
Average CPC= Total Cost of Clicks/ Total number of clicks
- Maximum Cost per Click: The highest amount you would want to pay for a click on the advertisement.
- Enhanced Cost per Click: Enhanced Cost per Click is an automated conversion bidding strategy for ads that will appear in Google’s Search Network and Display Network.
- Manual Cost per Click: Manual CPC is when advertisers set the maximum CPC for every ad manually rather than trusting the automated bidding strategies.
Benefits of calculating the Cost Per Click
These are the benefits of calculating the cost per click:
- It enables you to drive traffic to your website: Ads helps you attract more customers to your website. They pay publishers a fee to display your ads when the probability to visit your target audience is high.
- Helps you identify which ad types to use: CPC helps you identify that if the budget is not helping, you can shift your budget to ad types that generate high revenue.
- Choose manual or automated bidding strategies: CPC gives you an idea of ad spends. It also helps you to automate your bidding strategies to attract a target audience.
- Helps you improve paid advertising campaigns: Compare the revenue against the cost of paid advertising campaigns.
FAQs
What types of ads have a factor of CPC?
These types of ads have a factor of CPC:
- Shopping ads
- Image ads
- Video ads
- Text ads
- Facebook ads
- Instagram ads
- LinkedIn ads
- Twitter promoted tweets
What is a good CPC for Facebook Ads 2022?
Facebook bill advertisers depending on two metrics that include Cost Per Click (CPC) and Cost Per Mile (CPM). For Facebook Ads, advertisers are expected to pay $0.94 per click or $12.07 per 1000 impressions.
What is a good CPC for YouTube ads?
The ad price for YouTube depends on targeting and bidding options. For YouTube, average CPC expected is $0.49.
Which one is better: Low CPC or high CPC?
Every advertiser wants to have a low CPC because low CPC means that you can have more customers that can approach your website. It can lead to higher sales through potential leads.
Low CPC means higher return on investment because you get to earn more money than the amount you spend.



